Gas atomized powder is a type of metal powder produced through gas atomization, a process where molten metal is broken up into droplets and rapidly cooled by a high pressure gas stream. This method produces a very fine, spherical powder ideal for applications like metal injection molding, additive manufacturing, and surface coating processes.
How Gas Atomized Powder is Made
The gas atomization process starts by melting the desired metal in an induction furnace. Once the metal reaches the optimum temperature, it is poured in a thin stream into the atomization chamber. High pressure inert gas (usually nitrogen or argon) is forced through specialized nozzles, creating strong gas currents that break up the molten metal stream into very fine droplets.
As the droplets fall through the chamber, they rapidly solidify into powder particles due to the high surface area to volume ratio. The gas also prevents the particles from agglomerating. The powder falls through the chamber onto a collection screen where it is sifted to achieve the desired particle size distribution.
Key steps in gas atomized powder production
| Step | Sự miêu tả |
|---|---|
| Melting | Metal is melted in an induction furnace |
| Pouring | Molten metal is poured into the atomization chamber |
| Nguyên tử hóa | High pressure gas breaks up metal stream into fine droplets |
| Solidification | Droplets rapidly cool into solid powder particles |
| Collection | Powder is collected at the bottom of the chamber |
| Sàng lọc | Powder is sieved to achieve target particle size distribution |
Benefits of Gas Atomized Powder
Some key advantages of gas atomized powder include:
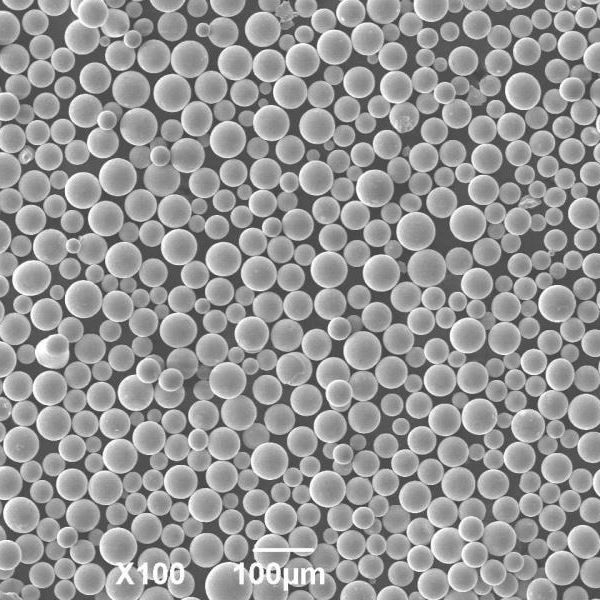
- Hình thái hình cầu – The droplets solidify into very spherical particles ideal for sintering and melting.
- Fine particle size – Particle sizes ranging from 10 – 150 microns can be achieved. Much finer than other methods.
- Narrow distribution – The particle size distribution is very narrow, improving sinterability.
- Độ tinh khiết cao – The inert gas prevents oxidation and minimizes contamination.
- Good flowability – Spherical shape improves powder flow characteristics.
- Wide applicability – Most metals and alloys can be gas atomized into powder.
These properties make gas atomized powders well suited for metal injection molding, additive manufacturing, and advanced sintering applications. The high purity and spherical morphology result in excellent densification behavior.
Metals and Alloys Used for Gas Atomization
| Vật liệu | Ví dụ |
|---|---|
| Thép không rỉ | Austenitic, ferritic, duplex, and martensitic stainless steels like 316L, 17-4PH, 420 |
| Thép công cụ | H13, M2 |
| Cobalt alloys | Đầu bếp |
| Nickel alloys | Inconel, Rene |
| Hợp kim Titan | Bạn-shal-hv |
| Refractory metals | Tungsten, molybdenum, tantalum |
| Copper alloys | Brass, bronze, copper |
| Hợp kim nhôm | 6061 aluminum |
| Precious metals | Silver, gold, platinum group |
- Thép không rỉ – Austenitic, ferritic, duplex, and martensitic stainless steels are commonly gas atomized. Grades like 316L, 17-4PH, and 420 are popular.
- Thép công cụ – Tool steels like H13 and M2 can be atomized. Used for molding tooling components.
- Cobalt alloys – Biocompatible cobalt alloys for dental and medical uses like CoCrMo.
- Nickel alloys – Superalloys like Inconel and Rene alloys are gas atomized for turbine components.
- Hợp kim Titan – Ti-6Al-4V alloy powder for aerospace components and implants.
- Refractory metals – Tungsten, molybdenum, tantalum commonly atomized.
- Copper alloys – Brass, bronze, and copper atomized for electronic/electrical uses.
- Hợp kim nhôm – Aluminum 6061 commonly atomized for automotive and aerospace.
- Precious metals – Silver, gold, platinum group metals atomized for jewelry uses.
Nearly any alloy that melts without decomposing can be gas atomized if parameters like melt superheat and gas pressure are optimized.
Related Products:
Typical Particle Size Distribution
Gas atomized powders are characterized by their particle size distribution. This gives an indication of the average size and range of powder sizes produced. A typical particle size distribution may look like:
| Particle Size (microns) | Percentage |
|---|---|
| 10-25 | 10% |
| 25-45 | 40% |
| 45-75 | 30% |
| 75-105 | 15% |
| 105-150 | 5% |
- Majority of particles are in the 25-75 micron range
- Minimum particle size around 10 microns
- Maximum around 150 microns
- Narrow distribution with standard deviation around 30 microns
The particle size range and distribution influences the powder properties and application suitability. Finer distributions are used for micro molding while coarser sizes for kinetic spraying.
How to Choose Suitable Gas Atomized Powder
Here are some recommendations on selecting the right gas atomized powder for your application:
- Match the alloy composition to your end use requirements like corrosion resistance or high temperature strength.
- Consider particle size based on intended use. Finer powders (~15 μm) for micro MIM, coarser (~60 μm) for cold spraying.
- Spherical morphology above 90% ensures maximum density with sintering or melting.
- Narrow particle size distribution improves flow and enhances green density.
- Higher purity and lower oxygen content powder for improved mechanical properties.
- Steels typically atomized in argon, reactive alloys like titaniums in nitrogen atmosphere.
- Choose reputable powder suppliers that can provide complete analysis reports.
- Consider atomization process parameters used by supplier to ensure suitable powder characteristics.
- Request samples to run evaluations and tests before purchasing large quantities.
How Gas Atomized Powder is Used
| Ứng dụng | Sử dụng |
|---|---|
| Đúc kim loại | Fine powders for micro MIM, high powder loading, spherical morphology for strength |
| sản xuất phụ gia | Spherical morphology for SLS/DMLS, fine powders for binder jetting |
| Xịt nhiệt | Gas atomized feedstock for cold spray, fine distribution for solution precursor spraying |
| Surface Engineering | Spherical powder for kinetic metallization, powder coating |
Đúc kim loại (MIM)
- Finer gas atomized powders for micro MIM of small, complex parts.
- Excellent flowability allows high powder loading and green density.
- Spherical morphology gives superior sintered strength and density.
sản xuất phụ gia
- Ideal spherical morphology for powder bed fusion processes like selective laser sintering (SLS) and direct metal laser sintering (DMLS).
- Inert gas atomization improves powder reuse due to low oxygen content.
- Fine powder used in binder jetting and inkjet metal printing processes.
Xịt nhiệt
- Gas atomized feedstock preferred for high velocity spray processes like cold spray.
- Dense coatings from deformation of ductile, spherical powder particles on impact.
- Finer powder distributions for suspension and solution precursor spraying.
Surface Engineering
- Spherical powders allow smooth surface finish in kinetic metallization processes.
- Excellent flowability suits powder coating processes for corrosion and wear protection.
- Fine controlled sizes for surface texturing and grading applications.
Challenges Associated with Gas Atomized Powder
While having many benefits, gas atomized powder also comes with some challenges:
- High upfront capital investment for gas atomization equipment.
- Requires technical expertise to operate and optimize atomization process.
- Can be prone to oxidation if handling and storage not proper.
- Spherical powder morphology makes it harder to achieve high green density in pressing.
- Fine powders prone to dusting issues during handling and processing.
- Costly compared to water atomized and pre-alloyed powders.
- Contamination risks from improper gas atomization atmosphere.
- Variable quality between different powder suppliers and grades.
Proper steps must be taken to minimize these issues to gain the full advantages of gas atomized powder.
Recent Advances in Gas Atomized Powder Technology
Some newer developments in gas atomized powder production include:
- Multi-nozzle atomization for higher powder yields and faster production.
- Close-coupled atomization to minimize melt oxidation.
- Smooth powder production from ultrasonic gas atomization.
- Novel gas atomizing gases like helium for finer atomization.
- Gas conditioning systems to recycle and purify atomizing gas.
- Advanced screening techniques for tighter particle size distributions.
- Specialized gas atomizer designs for reactive alloys like magnesium and aluminum.
- Automated powder handling systems to minimize contamination.
- High pressure micro-nozzle atomization for submicron powder sizes.
- Integrated powder production, handling, and quality control systems.
Các câu hỏi thường gặp
Here are some common FAQs about gas atomized powders:
Q: What is the major advantage of gas atomized powder?
A: The very spherical particle morphology produced by gas atomization is the biggest advantage. This leads to excellent flow and compaction properties.
Q: What industries use gas atomized powder the most?
A: The automotive and aerospace industries are major consumers of gas atomized powder for metal injection molding and additive manufacturing.
Q: What is the typical gas used for atomization of steels?
A: Most steels are gas atomized using either nitrogen or argon gas due to their inert properties.
Q: How small can gas atomized powder particles be made?
A: Using specialized micro-nozzle atomizers, gas atomized powders with particle sizes below 1 micron are possible. Normal range is 10-150 microns.
Q: Can gas atomized powders be alloyed?
A: Yes, pre-alloyed gas atomized powders are produced by first melting and mixing alloys before atomizing.
Q: What causes satellites in gas atomized powder?
A: Satellites are caused by incomplete breakup of molten metal into fine droplets. Higher gas pressure reduces satellites.
Q: Does gas atomized powder have good sintering properties?
A: The spherical morphology and high purity of gas atomized powder lead to excellent sintering behavior. Over 98% density can be achieved.
Q: How are reactive metals like titanium and magnesium gas atomized?
A: Reactive metals are atomized using an inert gas containment system that prevents exposure to oxygen and nitrogen.
This covers the key aspects of gas atomized powder production, properties, applications, and technology. Let me know if you need any clarification or have additional questions!


