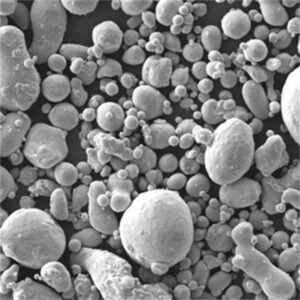
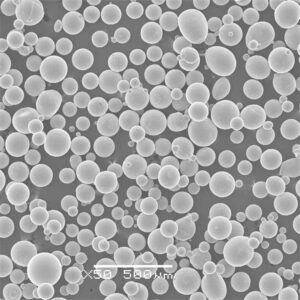
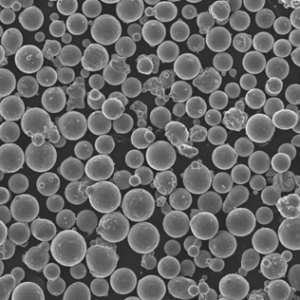
Overview of tungsten metal powder
Tungsten metal powder refers to fine particulate material composed primarily of elemental tungsten for use in various industrial applications. Key properties include extremely high density, strength, hardness, and high temperature durability.
Common applications of tungsten powder include:
- Tungsten carbide composites
- Tungsten heavy alloys
- Thermal spray coatings
- Additive manufacturing
- Electrical contacts
- Radiation shielding
Tungsten is considered a critical raw material for its unique performance combined with precarious supply dynamics. Continue reading to learn more about specifications, processing, pricing and uses of tungsten powder.

Material Types of tungsten metal powder
Tungsten metal powder comes in several primary compositions:
| Type | Typical Grades | Composition |
|---|---|---|
| Pure Tungsten | 99.9%, 99.99% purity | Elemental tungsten with impurity limits |
| Oxide-Dispersed Tungsten | Y2O3 additions | Tungsten with 0.5-1% yttrium oxide nanoparticles |
| Doped Tungsten | Lanthanum or other dopants | Tungsten with added grain growth inhibitors < 1% level |
Table 1: Common material categories for tungsten metal powders depending on application needs
Special dopants or oxide additives help tailor powder properties during consolidation into end-user components and parts requiring stability at high temperatures.
Key Properties
| Property | Typical Value | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 19.3 g/cc | Provides excellent mass and radiation blocking |
| Melting Point | 3410°C | Retains strength at extreme temperatures where most metals fail |
| Ultimate Tensile Strength | 550-620 MPa | Relatively brittle material with moderate tensile ductility |
| Hardness | HV 300-350 | Harder than tool steel |
| Young’s Modulus | 350-410 GPa | Stiff, resistant to deflection |
| Thermal Conductivity | 165 W/mK | Useful in thermal management parts operating at high temps |
Table 2: Overview of mechanical and physical properties exhibited by tungsten metal powder and consolidated alloys
The unrivaled temperature resistance combined with density drives adoption in demanding energy, aerospace, defense and electronics applications.
Particle Characteristics of tungsten metal powder
Typical tungsten powder morphology:
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Purity | 99.9% to 99.999% available |
| Particle shape | Irregular, angular |
| Size distribution | 1 to 100 micron typical |
| Oxygen content | <100 ppm |
| Surface oxide level | <50 nm thicknes |
Table 3: Powder quality metrics for tungsten metal powders used in various consolidation processes
Care must be taken to prevent oxidation during powder handling. Chemistries tailored to final part density and grain structure targets.
Production Process
- Primary methods to produce tungsten metal powder:
- Hydrogen Reduction (Hydrogen is used to convert oxide feedstocks to powder)
- Thermite Process Reduction (Exothermic oxide-metal reactions produce powder)
- Secondary mechanical processes:
- Jet Milling (Feedstock crushed into fine particles via collisions)
- Rotating Electrode Process (Electrode spinning and melt disintegration)
- Typical powder-part consolidation techniques:
- Hot Isostatic Pressing
- Sintering
- Additive Manufacturing (SLM, EBM)
- Environment and handling considerations:
- Nominally inert storage <40°C under argon
- Glove box handling to prevent oxidation
Applications of tungsten metal powder
Major uses of tungsten metal powder across industries:
| Segment | Application | Reason for Use |
|---|---|---|
| Industrial | Tungsten carbide materials | Extreme hardness and toughness for machining and mining tools |
| Defense | Kinetic energy penetrators | Superior density properties |
| Aerospace | Rocket engine nozzles | Maintains material strength in extreme environments |
| Energy | Heat shields, plasma torch components | High temperature performance where alternatives fail |
| Electronics | Electrical contacts | Arcing resistance combined with thermal/conductivity properties |
Table 4: Overview of key application areas for tungsten metal derived components in various industries
Tungsten sees ubiquitous use in products where hardness, density, toughness and strength are essential under extreme temperatures or loading.
Cost Analysis
Typical tungsten powder pricing:
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Powder Price | $50 to $350 per kg |
| Consolidated Part Price | $100+ per kg |
| Processing Yield | 60-70% |
| Primary Suppliers | China, Austria, Portugal, USA, Russia other countries |
| Lead Times | 6-12 weeks frequently |
Table 5: Buying factors including raw material costs for tungsten products
Consumers report extreme pricing volatility making budgetary planning difficult in the tungsten market. Established partnerships and supply agreements mitigate risks.
Pros and Cons
Advantages
- Extremely high density helps radiation shielding
- Maintains strength to over 3000°C where most metals melt
- Relatively neutral material avoids contamination
- Powder form supports complex geometries with some AM processes
- Hardness similar to tool steel once parts consolidated
Disadvantages
- Brittle characteristics mean low tensile ductility
- Difficult to fully densify parts without pinholes and voids
- Requires specialized cold-wall vacuum equipment for melting
- Risk of supply chain disruptions impacting availability
- Oxidation risk necessitates controlled handling
- Very expensive compared to steel alternatives
FAQ
Q: What particle size range is typical for tungsten powders used in various applications?
A: Most common size distributions fall between 1-100 microns. Finer particles pack better aiding full densification but have handling issues. Particle engineering depends on consolidation method with AM range generally 10-45 microns and carbide composites using up to sub-micron powders.
Q: What alloying elements can be incorporated into tungsten metal powder?
A: Typical alloyants like nickel, iron and copper severely degrade high temperature performance so are rarely added. Rhenium improves ductility slightly. Oxide particles help pin grain size. Rare earth dopants also stabilize properties. Alloying options are limited to small additives to maintain purity.
Q: What recommended storage and handling precautions apply for tungsten powders?
A: Like other air sensitive materials, tungsten metal powder should be kept below 40°C under inert argon gas to prevent oxidation from moisture or oxygen. Glove box protocols are necessary including leak checks. Never allow contact with organics during handling to prevent contamination or reactions.
Q: Does tungsten powder require hazardous material classification and special shipping?
A: Elemental tungsten metal powder is benign and not reactive. It qualifies for normal freight shipping in approved packaging similar to other industrial raw materials. No special DG classification needed unlike carbide grades with controlled cobalt content considered hazardous mixtures.
Q: What downstream parts production processes are compatible with tungsten powder feedstocks?
A: Hot isostatic pressing and sintering generate standard consolidated components like weights or heat shields. Additive manufacturing via powder bed fusion creates complex geometries unattainable otherwise. Powders also serve thermal spray coating feedstocks requiring post-consolidation.