Overview
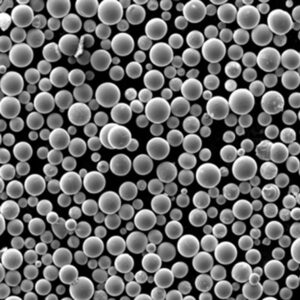
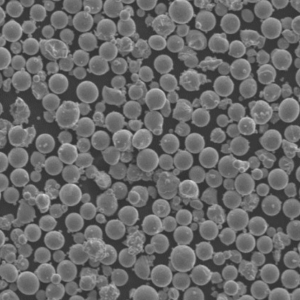
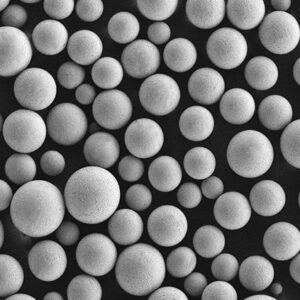
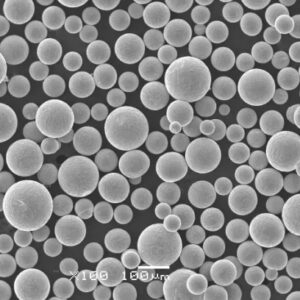
Plasma rotating electrode process (PREP) powder is a type of spherical powder made using the PREP method. PREP powders have unique properties that make them suitable for use in various applications like thermal spray coatings, metal additive manufacturing, and metal injection molding.
Some key features of PREP powder include:
- Highly spherical morphology with smooth surface
- Controlled microstructure with fine grain size
- Low porosity and high density
- Excellent flowability and spreadability
- High packing density
- Good blending characteristics
- Capability to manufacture alloys and composites
PREP enables customization of powder characteristics like particle size distribution, composition, density, oxide content, and more. By controlling the PREP process parameters, powders can be engineered for specific application requirements.
Types of PREP Powders
| Powder Material | Composition | Key Properties and Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Nickel alloy | NiCr, NiCrAlY, NiCoCrAlY | Oxidation and corrosion resistance. Thermal spray coatings. |
| Cobalt alloy | CoCr, CoCrAlY, CoNiCrAlY | High temperature strength. Thermal spray coatings. |
| Stainless steel | 316L, 304L | Corrosion resistance. Metal AM, MIM. |
| Tool steel | H13, P20 | High hardness. Metal AM, MIM. |
| Titanium alloy | Ti6Al4V, TiAl | High strength-to-weight ratio. Biomedical implants, aerospace. |
| Copper alloy | CuCrZr | High thermal conductivity. Electronic applications. |
| Aluminum alloy | AlSi12 | Lightweight. Automotive components. |
| Tungsten alloy | WNiFe, WCo | High density. Radiation shielding. |
Composition and Microstructure
PREP enables close control over powder composition and microstructural features:
- Alloying elements can be modified to achieve desired properties
- Microsegregation is minimized compared to gas atomization
- Fine grained microstructure with uniform distribution of phases
- Porosity and oxide content can be reduced to very low levels
- Spherical morphology is maintained after alloying
Key Properties of PREP Powder
| Property | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size distribution | PREP can achieve narrow distribution with controlled d50. | Ensures uniform melting and consistent properties. |
| Morphology | Highly spherical shape, smooth surface. | Excellent flow and packing density. |
| Apparent density | Can be optimized based on requirements. | Higher density improves powder spreading. |
| Flowability | Measured by Hall flowmeter method. | Ensures uniform powder feeding and spreading. |
| Packing density | High packing density up to 60%. | Maximizes volume fraction of metal powder in component. |
| Oxide content | Oxide levels below 0.2% achieved. | Reduces oxide inclusions in final part. |
| Microstructure | Fine grained and homogeneous. | Uniform property distribution in final part. |
| Surface chemistry | Chemistry precisely controlled. | Oxide formation, wettability, and spreading optimized. |
Applications of PREP Powder
PREP powder is used across various industries due to its specialized properties:
Thermal Spray Coatings
- Excellent flowability results in uniform feed rate and coating quality
- Controlled particle size distribution optimizes melting and minimizes unmelted powder
- Smooth surface morphology improves coating density and adhesion strength
- Low oxide content prevents oxide inclusions in coating
- Spherical shape gives higher deposition efficiency
Metal Additive Manufacturing
- High packing density allows more material per layer, reducing voids
- Smooth surface morphology results in uniform melting and melt pool flow
- Controlled particle size distribution prevents segregation issues
- Low surface oxide enables good inter-particle bonding
- Sphericity and flowability minimize powder feed problems
Metal Injection Molding
- High packing density maximizes sintered density
- Uniform particle size distribution prevents segregation
- Good flowability and compatibility results in homogenous mixing
- Low oxide content prevents sintering defects
- Controlled composition yields desired properties after sintering
Specifications
Typical specifications for PREP powder:
| Parameter | Range |
|---|---|
| Particle size | 10 – 150 microns |
| Particle size distribution | D10, D50, D90 can be controlled |
| Morphology | Highly spherical ≥ 0.9 |
| Apparent density | Up to 60% of theoretical density |
| Hall flowability | < 30 s/50 g |
| Oxide content | < 0.2 wt% |
| Microstructure | Fine grained < 10 microns |
| Surface chemistry | O, C, N levels precisely controlled |
Suppliers and Pricing
Some leading global suppliers of PREP powders are:
| Supplier | Location |
|---|---|
| Sandvik | Sweden |
| Praxair | USA |
| Hoganas | Sweden |
| CNPC Powder Group | China |
Pricing for PREP powder varies based on:
- Base metal (Ni, Co, steel)
- Alloy composition
- Particle size distribution
- Order quantity
- Level of customization
Indicative pricing ranges from $50/kg to $120/kg for common alloys. Custom alloys and particle size distribution can increase cost.
Comparison to Gas Atomized Powder
| Parameter | PREP Powder | Gas Atomized Powder |
|---|---|---|
| Particle shape | Highly spherical | Irregular, satellites present |
| Oxide content | Very low <0.2% | Typically 0.5-2% |
| Porosity | Near fully dense | Can have 10-20% porosity |
| Alloy homogenity | Excellent | Segregation prone |
| Flowability | Very good | Lower due to satellites |
| Packing density | Up to 60% | Typically 30-40% |
| Surface chemistry | Precisely controlled | Variable based on process |
| Cost | Higher | Lower capital cost |
Advantages of PREP Powder
- Excellent spherical morphology for flowability
- Controlled particle size distribution
- Low porosity and oxide content
- Alloy homogeneity and fine microstructure
- Customizable composition and properties
- High packing density for AM and MIM
Limitations of PREP Powder
- Higher cost compared to gas atomized powder
- Limited to smaller particle sizes, usually below 150 microns
- Requires advanced process control and optimization
- Limited production rate compared to gas atomization
- Restricted to select base metals like Ni, Co, and steels
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is plasma rotating electrode process (PREP) powder?
A: PREP powder is a highly spherical metallic powder produced using the PREP method which involves rotating an electrode in a plasma arc under precise control to achieve desired powder characteristics.
Q: What materials can be made into PREP powder?
A: Common materials include nickel, cobalt, stainless steel, tool steel, titanium, aluminum, and copper alloys. Other alloys and composites are also possible through PREP.
Q: What are the key advantages of PREP powder?
A: Key advantages are excellent sphericity and flowability, controlled particle distribution, low porosity and oxides, fine and uniform microstructure, customizable composition, and high packing density.
Q: What is PREP powder used for?
A: Major applications are thermal spray coatings, metal additive manufacturing, and metal injection molding due to its specialized properties.
Q: How is PREP powder different from gas atomized powder?
A: PREP powder has superior sphericity, lower oxides, less porosity, more homogenous composition and microstructure compared to gas atomized powder.
Q: Is PREP powder more expensive than gas atomized powder?
A: Yes, PREP powder typically costs more due to higher process complexity and control involved. But it offers significant performance advantages over gas atomized powder.
Q: What particle size is available for PREP powder?
A: The usual range is 10 to 150 microns. Both smaller and larger sizes are possible but less common. Particle size distribution can also be controlled as per requirements.
Q: Does PREP powder have limited alloy options?
A: PREP is most established for nickel, cobalt and stainless steel alloys. But ongoing process development is expanding the alloy systems possible, including reactive materials like titanium and aluminum.
Q: Can PREP powder be customized for specific applications?
A: Yes, customization is a key benefit of PREP. Particle characteristics and alloy composition can be tailored to meet requirements for thermal spray, AM, MIM, etc.