Tungsten powder with high density finds extensive use across industrial, military, and technology applications. This guide provides comprehensive information on the properties, production, applications, suppliers, and costs of high density tungsten powder.
Introduction to High Density Tungsten Powder
High density tungsten powder is a fine particulate form of tungsten metal known for its:
- Very high density up to 19.3 g/cm3
- High strength and hardness properties
- High temperature resistance
- Thermal/electrical conductivity
- Applications requiring high mass and durability
- Use in alloys, composites, radiation shielding, and more
With density almost twice that of lead, tungsten makes an ideal material for applications requiring weight, compact size, kinetic energy, and vibration damping. This guide details the different types, production methods, properties, applications, suppliers, costs, and other considerations for high density tungsten powder.
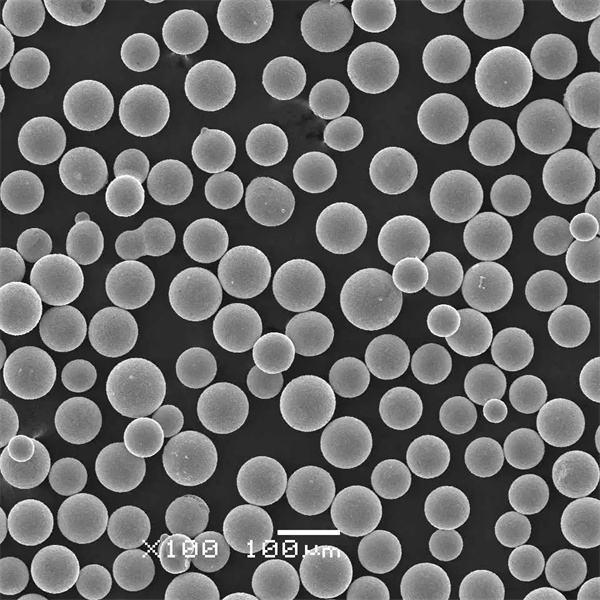
Types of High Density Tungsten Powder
Tungsten powder is available in different compositions and forms categorized by:
High Density Tungsten Powder Types
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Pure tungsten | Over 99.9% W, impurities like C, O, N, Fe |
| Tungsten heavy alloys | W with Ni, Fe, Cu, Co |
| Tungsten carbide | WC powder |
| Nanoscale tungsten | Ultrafine particle size under 100 nm |
| Spherical tungsten | Near-perfect rounded particle shape |
| Chemically reduced tungsten | Irregular morphology, high oxygen |
| Milled tungsten | Flattened/folded particles from milling |
- Pure tungsten provides the highest density but can be brittle. Alloying improves toughness and workability.
- Tungsten carbide boosts hardness and wear resistance significantly.
- Specialty grades like spherical and nano powder offer enhanced properties.
- Production method determines powder characteristics optimal for certain applications.
Production Methods for High Density Tungsten Powder
Tungsten powder can be produced through various techniques:
Tungsten Powder Production Methods
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Hydrogen reduction | Reduction of tungsten oxide using hydrogen |
| Thermal decomposition | Heating tungsten oxide in hydrogen atmosphere |
| Plasma atomization | Melted tungsten atomized using plasma torch |
| Electrode induction melting | Melted tungsten stream broken into droplets |
| Chemical reduction | Using reducing agents like ammonia on tungsten oxide |
| Mechanical milling | Ball milling tungsten into fine powder |
- Hydrogen reduction and thermal decomposition of tungsten oxide are common commercial production routes.
- Plasma atomization generates fine spherical powders suitable for additive manufacturing.
- Chemical reduction methods like ammonia can produce high purity powder.
- Mechanical milling via ball milling can grind tungsten into fine particle sizes.
- Alloy tungsten powder is produced by mixing elemental or prealloyed powders.
- Secondary processing like vacuum sintering, annealing, spraying, etc. further tailors powder qualities.
Properties of High Density Tungsten Powder
The unique properties of tungsten originate from its high atomic mass and make it ideal for demanding applications:
High Density Tungsten Powder Properties
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Density | 19.25 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 3422°C |
| Thermal conductivity | 173 W/mK |
| Electrical resistivity | 5.5 μΩ-cm |
| Tensile strength | 550-700 MPa |
| Elastic modulus | 400 GPa |
| Poisson’s ratio | 0.28 |
| Thermal expansion | 4.5 x 10<sup>-6</sup>/K |
- Highest melting point of all metals. Retains strength at high temperatures.
- Extremely high density provides excellent mass within a compact footprint.
- Good thermal and electrical conductivity.
- High elastic stiffness. Resists deformation under load.
- Alloying with Ni, Fe, Co, Cu can optimize combinations of strength, ductility, and density.
- Powder shape, size distribution, and processing conditions affect final part properties.
Applications of High Density Tungsten Powder
The unique properties of high density tungsten powder make it suitable for the following key applications:
High Density Tungsten Powder Applications
| Industry | Uses |
|---|---|
| Defense | Kinetic energy penetrators, ammunition, radiation shielding |
| Automotive | Tire studs, weights, vibration damping |
| Aerospace | Radiation shielding, counterweights |
| Electronics | Electrical contacts, heat sinks, sputtering targets |
| Medical | Radiation shielding, probes, surgical tools |
| Sports | Golf club weights, darts, fishing lures |
| Industrial | Drill bits, cutting tools, wear parts |
- Penetrators: Tungsten alloys make extremely dense kinetic energy projectiles for armor piercing ammunition.
- Radiation shielding: Tungsten’s density provides effective shielding from X-ray and gamma radiation in medical and defense sectors.
- Vibration damping: The high mass efficiently damps vibrations in machinery and vehicles.
- Electrical contacts: Tungsten’s conductivity and resistance to arcing is leveraged in switches, relays, and more.
- Heatsinks: High thermal conductivity enables heat dissipation in electronics.
- Wear parts: Extreme hardness resists wear even at high temperatures in cutting tools.
Global Suppliers of High Density Tungsten Powder
Some major companies supplying various grades of high density tungsten powder include:
High Density Tungsten Powder Suppliers
| Company | Headquarters |
|---|---|
| Wolfram Company | Austria |
| HC Starck | Germany |
| Xiamen Tungsten | China |
| JX Nippon Mining & Metals | Japan |
| Midwest Tungsten | USA |
| GTP | USA |
| H. Cross Company | USA |
| TaeguTec | South Korea |
- Leading suppliers have expertise in specialized production methods for high purity and advanced tungsten powder.
- Custom alloys, particle size distribution, morphology, coatings, and other specifications can be provided.
- A global supply chain and distribution network enables serving diverse markets.
- Smaller regional manufacturers also supply tungsten powder tailored for local industry needs.
Cost Analysis of High Density Tungsten Powder
As a rare metal, tungsten powder commands higher pricing than common metals like steel or copper powder:
Cost Drivers for High Density Tungsten Powder
- Purity levels and chemistry
- Particle shape and size distribution
- Purchase volumes
- Production process complexity
- Raw tungsten prices
- Supplier margins and location
Tungsten Powder Price Ranges
| Type | Price Range |
|---|---|
| Pure tungsten, standard grade | $40-100 per kg |
| High purity tungsten | $150-250 per kg |
| Tungsten heavy alloy powder | $50-150 per kg |
| Nanoscale tungsten powder | $200-2000 per kg |
- Higher purity levels increase cost. Specialty grades command a premium.
- Smaller particle sizes and spherical morphology are more expensive to produce.
- Large volume purchases can lower per-unit cost significantly.
- Location factors like transportation, import duties affect final pricing.
- Fluctuating supply-demand dynamics for raw tungsten impact pricing.
Standards and Certifications
Key standards applicable to tungsten powder composition, quality, and manufacturing include:
- ASTM B772: Standard Specification for Tungsten Base Powders
- ISO 18323: Specification for wrought tungsten
- ASTM B939: Radiation exposure testing of tungsten
- AMS 7999: Spherical tungsten powder specification
- ISO 9001: Quality management system certification
- REACH: Registration, Evaluation, Authorization and Restriction of Chemicals compliance in the EU
Factors to consider when purchasing:
- Supplier ISO 9001 certification and ASTM/ISO compliance
- Composition analysis and lot test certificates
- Industry-specific certifications as required
- Regulatory compliance for geographical regions
Tungsten vs. Depleted Uranium Comparison
Tungsten vs. Depleted Uranium Powder
| Parameter | Tungsten | Depleted Uranium |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 19.25 g/cm3 | 18.9 g/cm3 |
| Radioactivity | Non-radioactive | Low-level radioactive |
| Toxicity | Moderate | High from heavy metal toxicity |
| Cost | High | Low |
| Production | Conventional mining and processing | Byproduct of nuclear enrichment |
| Applications | Broad range | Restricted applications |
| Availability | Readily available | Limited supply |
- Tungsten has slightly higher density than depleted uranium.
- It offers non-radioactive, cost-effective high density compared to radioactive depleted uranium.
- Tungsten has lower environmental and health risks during material handling.
- Higher cost but easier availability makes tungsten attractive for commercial applications.
- Depleted uranium use faces regulatory restrictions and public perception issues.

Key Takeaways on High Density Tungsten Powder
- With density of 19 g/cm3, tungsten makes an extremely heavy and compact material.
- Major production routes are hydrogen reduction and thermal decomposition of tungsten oxides.
- Key applications leverage density for radiation shielding, projectiles, vibration damping, electrical contacts.
- Alloying with Ni, Co, Fe improves toughness and workability compared to pure tungsten.
- Leading mining and powder metallurgy companies offer various powder grades.
- Cost is higher than standard metals but lower than rare earths or precious metals.
- Compliance with international standards ensures suitability for industrial uses.
FAQs
Q: What is high density tungsten powder used for?
A: Main uses are radiation shielding, kinetic energy penetrators, counterweights, tire studs, electrical contacts, heat sinks, and vibration damping leveraging its very high density.
Q: Is tungsten powder toxic?
A: Tungsten powder is not highly toxic but inhalation of fine powders can pose a respiratory hazard requiring protective measures during handling.
Q: What is the difference between tungsten and tungsten carbide powder?
A: Tungsten carbide (WC) powder is extremely hard and wear resistant. Tungsten metal powder has higher toughness and thermal/electrical conductivity.
Q: How is tungsten powder made?
A: Major production methods are direct hydrogen reduction, thermal decomposition, plasma atomization, chemical reduction, and mechanical milling of tungsten oxides to tungsten powder.
Q: Why is high density tungsten used in military applications?
A: The extreme density makes tungsten ideal for armor piercing kinetic energy penetrators that rely on momentum transfer and resistant radiation shielding.
Q: What are some examples of tungsten alloys?
A: Common alloys include tungsten-nickel-iron, tungsten-nickel-copper, and tungsten-silver used when easier machining and forming is required.
Q: Is tungsten environmentally hazardous?
A: Tungsten metal itself has relatively low environmental risks but processing of ores and dust inhalation require proper controls and personal protection.
Q: What is nano tungsten powder?
A: Nano tungsten powders have ultra-fine particle sizes under 100 nm (0.1 microns). Nanostructure enhances strength, reactivity, sintering, and other properties.
Q: Is tungsten powder flammable or explosive?
A: Like most metals, tungsten powder itself is not flammable or explosive under normal conditions. But fine dust when mixed with air can pose a fire or explosion risk requiring precautions.
Q: Where is tungsten primarily mined?
A: China accounts for over 80% of global tungsten mine production, followed by Russia, Canada, Bolivia, Austria, and Portugal as leading producers.