Niobium metal powder has found expanding uses across medical devices, electronics, optics, aerospace, and other advanced fields in recent years. This guide takes an in-depth look at spherical niobium powder specifically engineered to deliver enhanced properties and performance.
We’ll survey everything from composition and characteristics to production methods, applications, suppliers, specifications, costs, and more surrounding this unique material. Let’s get started!
Introduction to Spherical Niobium Powder
Niobium, also known as columbium, sits beside its sister metal tantalum in group 5 of the periodic table. Pure niobium offers a rare combination of properties:
- Low density but high strength
- Thermal stability and oxidation resistance
- Superconductivity at low temperatures
- Compatibility with living tissues
These make niobium an important specialized material today. And using the metal in spherical powder form unlocks additional capabilities.
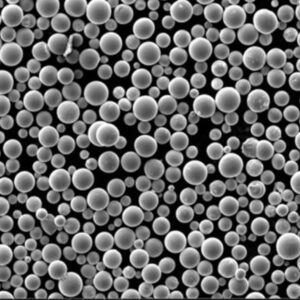
Spherical Morphology Benefits
Microscopically round niobium particles feature improved flow and handling over irregular flakes. Spherical shape also enhances packing density.
This means spherical powders 3D print, sinter, and process better across the board. We’ll revisit these advantages in more detail later. But first, let’s further analyze spherical niobium powder composition and production.
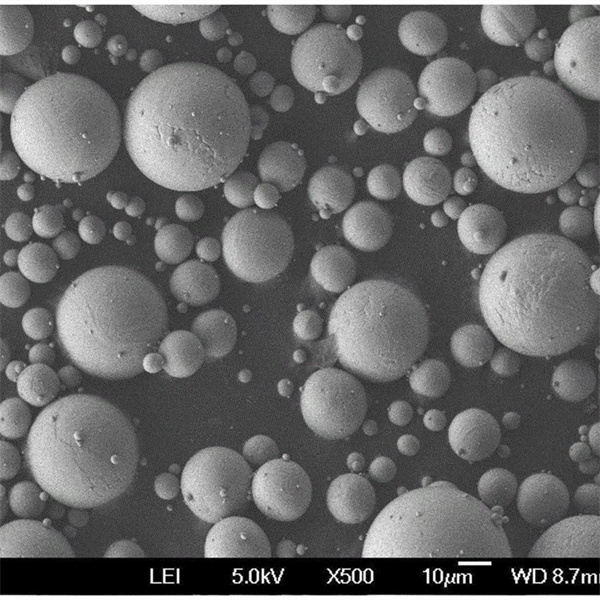

Niobium Powder Composition
Pure niobium metal sees niche uses. But niobium-based alloys and compounds expand applications further through optimized material properties.
Major Niobium Alloy Types:
| Alloy | Major Elements | Notable Properties |
| Vacuum grade niobium | Nb + N/O/C/H | Highest purity |
| Nb-Zr alloys | Nb + Zr | Precipitation strengthening |
| Nb-Ti alloys | Nb + Ti | Superconductivity |
| Niobium nitride | NbN | Hardness, conductivity |
- Vacuum-grade niobium aims for highest purity levels with other elements limited to just 10s of ppm
- Zirconium, titanium, and molybdenum alloyed with niobium produce precipitation-hardened materials
- Niobium nitride ceramic material formed by nitrogen absorption during sintering increases hardness
Production Methods:
| Method | Description |
| Vacuum Arc Melting | Melting pure Nb ingot in water-cooled crucible under vacuum and remelting to achieve homogenous solid |
| Electron Beam Melting | Using electron beams as high intensity heat source to melt and drip molten niobium under vacuum atmosphere into fine droplets |
| Hydrogenation-Dehydrogenation | Reacting niobium powder with hydrogen gas at temperatures up to 600°C to make NbH powder and then removing the hydrogen later |
Vacuum processed spherical Nb powder offers high chemical purity essential for performance. Now let’s analyze the key physical characteristics.
Properties of Spherical Niobium Powder
Optimized spherical morphologies tune physical, chemical, mechanical, electrical and other performance properties. Exact powder characteristics depend on the intended application.
But common traits of leading spherical niobium powders include:
Particle Size Distribution
- Typical size range between 1-250 microns
- Median particle sizes of 10-45 microns preferred
- Controllable particle sizes and tight distributions
- Minimized satellite content below 5%
Particle Shape
- Highly spherical morphology
- Smooth powder surface
- Shape consistency from batch-to-batch
- Solid internal structure with low porosity
- Chemically homogenous throughout
Powder Flow
- Excellent flowrates, typically >25s/50g
- Fluid flow handling down to sub-micron sizes
- Mixes and blends evenly with other powders
- Wide range of packing densities achievable
Purity Levels
- Oxygen below 200 ppm
- Nitrogen below 50 ppm
- Carbon below 250 ppm
- No nitride or carbide inclusions
- 99.99% pure Nb content or better
Density
- Apparent density from 2-12 g/cm3
- Tap density reaching 70% of pure Nb solid density
- True density 8.57 g/cm3
With deeper insight into spherical powder composition, manufacturing, and attributes, let’s now explore some key applications leveraging these unique advantages.
Applications of Spherical Niobium Powder
Aerospace and Defense
- High-performance engines and turbines
- Lightweight structural brackets
- Missilecomponents
- Radar absorption
- Satellite sub-systems
Quantum Science
- Superconducting magnets
- Quantum computing
- Particle accelerator targets
- MRI contrast agents
- Medical tracers
Electronics
- Capacitors and resistors
- 5G antennas
- Conductive films
- Vacuum tubes
- Waveguides
Optics
- Camera lenses
- Security inks
- Optical filters
- Anti-reflective coatings
Chemical Processing
- Acid plants
- Chloride production
- Catalysts
- Metal winning
Energy
- Nuclear reactors
- Fusion experiments
- Hydrogen storage
- Battery materials
Niobium’s unique capabilities lend well to advanced applications like superconductors, medical devices, specialty alloys, optics, electronics, and chemical production.
Delivering niobium’s promising performance in products starts with spherical powder feedstock optimized for fabrication processes like metal AM or sintering.
Now let’s overview popular techniques to manufacture precision niobium-based components from spherical powders.
Fabrication with Spherical Niobium Powders
Special spherical morphology and tight size distributions of engineered niobium powders tailor them for modern fabrication needs:
Additive Manufacturing
- Selective laser melting (SLM)
- Electron beam melting (EBM)
- Binder jetting
- Laser powder bed fusion (PBF)
- Directed energy deposition
Conventional Powder Processing
- Press and sinter
- Hot isostatic pressing (HIP)
- Metal injection molding (MIM)
- Thermal spray
- Granulation
Top Benefits of Spherical Powder
- Increased packing density for reduced porosity
- Enhanced powder flow and spreading
- More uniform heating and melt pool dynamics
- Reduced residual stresses and cracking
- Good interlayer bonding improved surface finish
- Higher production yield
Spherical particles 3D print better quality niobium components with fine resolution, precision geometries, controlled microstructures and customizable interior features.
These same advantages apply to pressing and sintering niobium powders into high performance parts too.
Now let’s spotlight some leading global suppliers providing quality spherical niobium powder today.
Leading Spherical Niobium Powder Suppliers
| Producer | Product Designations |
| CBMM | High purity niobium micro and nanopowders |
| HC Starck Solutions | Pure niobium and niobium alloys |
| H.C. Starck Tantalum and Niobium | Spherical niobium powders |
| ESPICorp | Ultra high purity niobium hydride powder |
| American Elements | Niobium metal powder and compounds |
These major metal powder producers offer extensive expertise working with niobium and its alloys. Unique in-house manufacturing capabilities also allow tailored powder morphologies.
Now let’s examine key quality metrics and compliance standards required by niobium powder specifications.
Niobium Powder Specifications
Applications demand consistency. So standardized test methods from organizations like ASTM help define and control spherical niobium powder quality:
Quality Standards:
| Organization | Standard Test Methods |
| ASTM | B809, B829, F3049 |
| ISO | 4497-2 |
These cover critical metrics like:
- Particle size distribution
- Powder morphology and surface area
- Apparent and tap density
- Flow rate through fixed funnel
- Loss on ignition
- Chemical assays
- Phase analysis
Meeting application needs requires tight control of these powder characteristics. Leading global niobium suppliers have quality systems implementing the latest versions of these test methods.
Now let’s examine niobium powder cost considerations.
Niobium Powder Pricing
As a specialized minor metal, niobium commands higher prices driven by raw material scarcity and processing complexity. Nonetheless, niobium delivers unmatched performance per pound in many cases.
Price Influencing Factors:
- Purity grade – From 98% to 99.99%
- Powder size range – Nanoscale costs more
- Order quantity – Bulk buys save 20-40%
- Delivery times – Quick turn “express fee”
- Additional validation testing
Cost Examples:
- 99% pure 2-7 micron niobium powder – $200-$500 per kg
- 99.8% pure niobium nanopowder <250 nm – $1000-$2000 per kg
While costs exceed common metals, unique properties justify niobium’s use where performance matters most. And recycling powders can offset expenses too.
Now let’s answer some common questions about niobium powder.
FAQs
Here are answers to some frequently asked questions about this unique material:
What is niobium primarily alloyed with to enhance different properties?
Common niobium alloys include NbTi for superconductivity, NbZr for strength, NbMo for high-temp use, and NbN ceramics for hardness and conductivity.
What is the benefit of vacuum grade niobium powder?
Ultra-high purity with less contaminants allows reliably achieving niobium’s best intrinsic properties – density, strength, conductivity, superconductivity, etc.
Why is flowability important for niobium powder intended for AM or sintering uses?
Good powder flow ensures excellent spreading and uniform layers needed to tightly pack particles. This minimizes defects while 3D printing or pressing/sintering.
What is hydrogen embrittlement and why is it a concern for niobium applications?
During heating, residual hydrogen from powder production processes can make some metals brittle. Careful vacuum degassing and handling of niobium is performed to prevent this.
How is niobium recycled after use in applications like superconducting medical scanners?
Recovery techniques like hydriding allow niobium to be reclaimed and reduced to powder again for reuse. This saves resources while meeting demand.