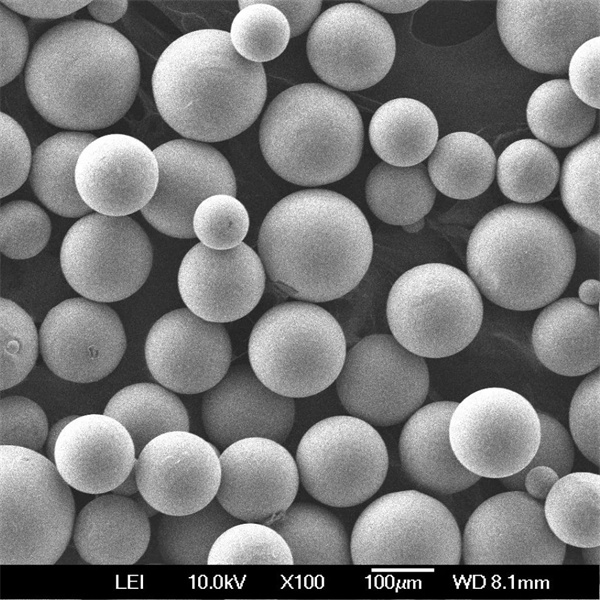
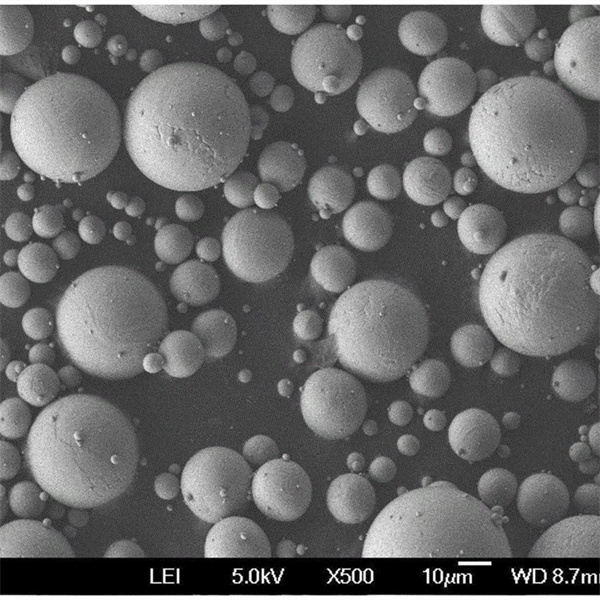
TiNbZrSn Alloy Powder
TiNbZrSn alloy powder is an advanced composite material with exceptional properties making it suitable for a wide range of demanding applications. This article provides a comprehensive overview of TiNbZrSn powder including its composition, characteristics, production methods, applications, suppliers, and more.
Low MOQ
Provide low minimum order quantity to meet different needs.
OEM & ODM
Provide customized products and design services to meet unique customer needs.
Adequate Stock
Ensure fast order processing and provide reliable and efficient service.
Customer Satisfaction
Provide high quality products with customer satisfaction at the core.
share this product
Table of Contents
TiNbZrSn Alloy Powder Composition
TiNbZrSn alloy powder consists of the following elements:
| Element | Weight % |
|---|---|
| Titanium (Ti) | 35-40% |
| Niobium (Nb) | 35-40% |
| Zirconium (Zr) | 5-10% |
| Tin (Sn) | 5-10% |
This precise combination of titanium, niobium, zirconium and tin results in an alloy with outstanding strength, hardness, and elasticity compared to conventional alloys. The niobium content in particular significantly enhances the mechanical performance.
By carefully controlling the ratios of the constituent metals, the properties of the alloy powder can be optimized for different applications requiring high strength-to-weight characteristics, corrosion resistance, biocompatibility, or high-temperature durability.
TiNbZrSn Alloy Powder Properties
TiNbZrSn alloy powder exhibits the following exceptional properties:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| High strength | Yields strength over 1400 MPa, on par with advanced aerospace alloys |
| Low density | Density around 6.5 g/cm3, much lower than steel |
| Excellent elasticity | Young’s modulus around 100 GPa, enabling flexibility |
| High hardness | Vickers hardness over 450 HV, better abrasion resistance than stainless steel |
| Good corrosion resistance | Resists corrosion in harsh environments |
| Biocompatibility | Non-toxic and suitable for medical implants |
| High melting point | Melting above 2500°C making it viable for high temperature applications |
The combination of high strength, low weight, hardness and elasticity is rare and makes TiNbZrSn an extremely versatile material. It outperforms conventional alloys like stainless steel across multiple properties.
TiNbZrSn Alloy Powder Production
TiNbZrSn alloy powder can be produced using the following advanced methods:
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Gas atomization | Molten alloy sprayed into fine droplets which solidify into powder |
| Plasma rotating electrode process (PREP) | Electrode rotates rapidly in plasma arc to disintegrate into powder |
| Hydride-dehydride (HDH) | Alloy is hydrogenated, mechanically crushed into powder, then de-hydrogenated |
Gas atomization allows control over particle size distribution and results in smooth spherical powder ideal for additive manufacturing. PREP and HDH methods allow economical production of irregular powder suitable for pressing and sintering.
The alloy composition can be precisely maintained in these powder production processes, ensuring consistent properties. High purity inert gas atmospheres prevent contamination.
TiNbZrSn Alloy Powder Applications
Thanks to its well-balanced material properties, TiNbZrSn alloy powder is used in the following applications:
| Industry | Application |
|---|---|
| Aerospace | Aircraft and rocket engine components, space systems |
| Automotive | Valve springs, fasteners, actuators |
| Medical | Implants, prosthetics, devices |
| Defense | Armor, munitions, ballistics |
| Additive manufacturing | 3D printed parts with high strength |
| Chemical processing | Corrosion resistant vessels, piping |
The combination of strength, hardness, and biocompatibility makes TiNbZrSn suitable for load-bearing implanted devices like hip and knee joints. Its corrosion resistance suits it for seawater-exposed naval applications. And its high-temperature durability is an advantage in jet engines and turbines.
Compared to conventional alloys, TiNbZrSn enables lighter, stronger and longer-lasting components giving it an edge in demanding industries.
TiNbZrSn Alloy Powder Specifications
TiNbZrSn alloy powder is commercially available in the following specifications:
| Attribute | Details |
|---|---|
| Particle sizes | 15-45 microns, 45-106 microns, 106-250 microns |
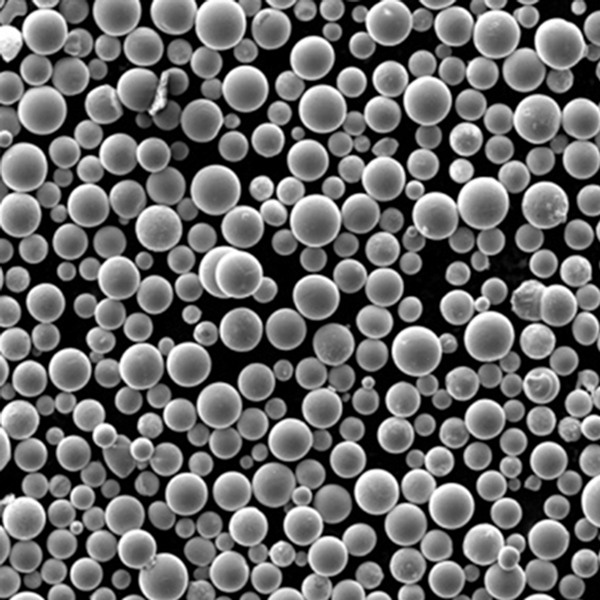
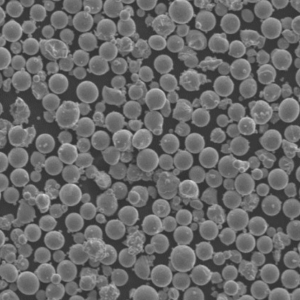
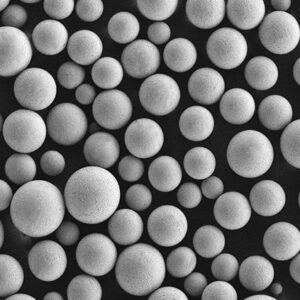
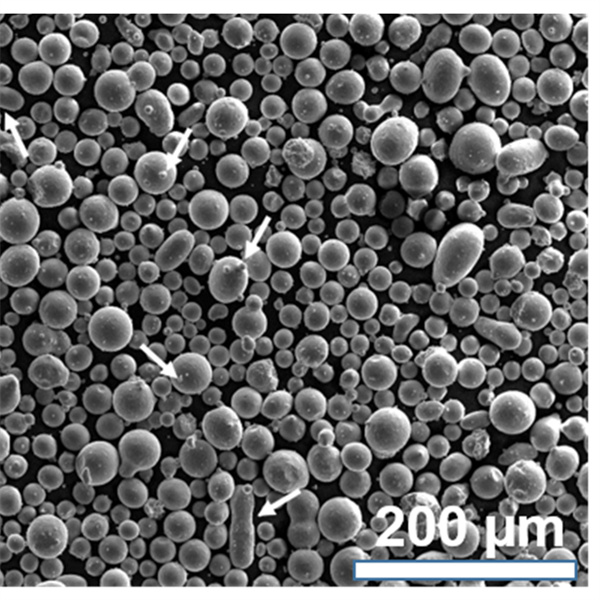
| Particle shape | Spherical, irregular |
| Purity | Up to 99.9% |
| Oxygen content | Under 2000 ppm |
| Powder grades | Grade 5, 23, 23 ELI |
| Supply form | Loose powder, sintered preforms |
Both gas atomized spherical powder and irregular powder from HDH or PREP is available. Smaller 15-45 micron powder is suited for additive manufacturing needing good flow and packing. Larger 106-250 micron powder is typically pressed and sintered.
Standards like ASTM F1805 and ISO 5832 provide composition limits and required properties for biomedical grade 23 ELI powder. Custom alloy compositions and particle sizes can also be produced to meet application requirements.
TiNbZrSn Alloy Powder Suppliers
Some leading global suppliers of TiNbZrSn alloy powder include:
| Supplier | Location |
|---|---|
| AMETEK | USA |
| CNPC Powder | China |
| GKN Hoeganaes | Europe |
| LPW Technology | UK |
| Sandvik Osprey | UK |
Reputable suppliers like these have advanced in-house powder production facilities using gas atomization or hydride-dehydride processes. They can provide various particle size distributions and customize the alloy composition as needed.
Small batch prototyping quantities to large commercial volumes are available. Strict quality control and testing is implemented by suppliers to ensure powder meets specifications.
TiNbZrSn Alloy Powder Pricing
As an advanced specialty alloy, TiNbZrSn powder commands a premium price:
| Powder Grade | Price Range |
|---|---|
| Grade 5 | $350-$500 per kg |
| Grade 23 | $450-$650 per kg |
| Grade 23 ELI | $550-$750 per kg |
The pricing depends on order quantity, particle size distribution, shape, and composition. Smaller quantities of fine spherical powder are more expensive. Irregular powder and larger batch sizes offer cost savings.
The pricing is several times higher than common alloys like 316L stainless steel powder. However, the superior properties justify the higher cost for critical applications needing maximized performance.
TiNbZrSn Alloy Powder Handling
To safely handle TiNbZrSn alloy powder:
- Store sealed containers in a cool, dry environment to prevent oxidation and hydration
- Avoid spillage to prevent powder accumulation as explosion hazard
- Ground all powder handling equipment and transport vessels
- Wear gloves and respiratory protection when handling powder
- Use non-sparking tools and vacuum systems with inert gas blanketing
- Employ ventilation and point-of-source fume extraction where required
The fine particle size makes TiNbZrSn powder flammable when dispersed. Careful handling following safety protocols is essential. Automated glove box handling and containment systems are recommended.
TiNbZrSn Alloy Powder Inspection
TiNbZrSn alloy powder should be inspected for:
| Parameter | Method | Acceptance Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Particle size distribution | Laser diffraction, sieving | Meets specified range |
| Particle shape | SEM imaging | Spherical, smooth surfaces |
| Particle chemistry | EDX/EDS, ICP-OES | Conforms to specified composition |
| Oxygen/nitrogen | Inert gas fusion | Under 2000 ppm oxygen |
| Apparent density | Hall flowmeter | Better flow for higher density |
| Flow rate | Hall flowmeter | Flows freely through aperture |
These tests ensure the powder meets specifications for size, shape, chemistry, cleanliness and flowability required for AM or press-and-sinter use.
TiNbZrSn Alloy Powder Testing
The following further tests may be done to qualify TiNbZrSn alloy powder:
| Test | Method | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Compressibility | Uniaxial pressing | Assess compaction response |
| Green strength | Transverse rupture strength | Measure strength before sintering |
| Density after sintering | Dimensional measurement | Ensure full consolidation |
| Microstructure | Optical microscopy, SEM | Assess melting, porosity, grains |
| Hardness | Vickers/Rockwell tests | Verify mechanical properties |
| Tensile strength | ASTM E8 | Measure UTS, yield, elongation |
Testing compressed and sintered samples is prudent to confirm powder processability and final mechanical properties versus design requirements.
TiNbZrSn Alloy Powder Pros and Cons
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Exceptional strength-to-weight ratio | Expensive compared to common alloys |
| Higher elasticity than other high-strength alloys | Lower ductility than titanium alloys |
| Excellent hardness and wear resistance | Requires careful handling due to reactivity |
| Resists corrosion in harsh environments | Difficult to machine and grind |
| Biocompatible for medical uses | Limited suppliers and availability |
| Withstands extremely high temperatures | Needs hot isostatic pressing for full consolidation |
For critical applications where performance outweighs cost, TiNbZrSn alloy powder delivers properties unmatched by other alloys. The main limitations are cost and availability.
Comparing TiNbZrSn to Other Alloys
How does TiNbZrSn compare to other high-performance alloy powders?
Versus stainless steel:
- 2x higher strength
- 70% lower density
- 5x higher hardness
- Better corrosion resistance
Versus titanium alloys:
- 50% higher elasticity
- 20% higher hardness
- Better creep resistance
- Lower ductility
Versus cobalt-chrome alloys:
- Lower density
- No toxic effects
- Higher service temperature
- Lower toughness
Versus Ni-based superalloys:
- Easier processing
- Lower cost
- Lower temperature capability
- Lower creep strength
So TiNbZrSn presents an optimal balance of properties not found in other alloys, making it suitable for the most demanding applications.
TiNbZrSn Alloy Powder Usage Insights
Here are some key insights on using TiNbZrSn effectively:
- Gas atomized powder with controlled particle size distribution flows and packs best for AM
- Irregular powder requires higher pressures for compacting and sintering
- Hot isostatic pressing helps achieve maximum density and properties
- Annealing can be used to tailor ductility and toughness as needed
- Near-net-shape parts minimize costly machining of sintered components
- Surface treatments improve wear resistance for sliding contact applications
- Joining dissimilar materials to TiNbZrSn requires selection of suitable process
- Tight supplier qualifications and testing helps ensure powder quality and performance
Understanding processing-microstructure-property relationships is important to harness the full potential of this exceptional alloy.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some common FAQs about TiNbZrSn alloy powder:
Q: Is TiNbZrSn powder compatible with 3D printing?
A: Yes, gas atomized TiNbZrSn with controlled particle size and high sphericity can be used for powder bed fusion and directed energy deposition AM processes. Parameters need optimization to achieve high density.
Q: What particle size is best for additive manufacturing?
A: 15-45 microns is recommended, ensuring good powder flow and packing. Larger sizes up to 106 microns have also been successfully printed for some applications requiring thicker layers.
Q: Does TiNbZrSn require hot isostatic pressing after AM?
A: HIP helps maximize density, eliminate internal pores and improve mechanical properties. But for some less demanding applications, as-printed TiNbZrSn parts may meet requirements without HIP.
Q: Can you machine and grind TiNbZrSn alloy?
A: Yes, but it requires rigid setups, high pressure coolant, sharp carbide tools and fine abrasives. Feed rates and speeds need to be lower than conventional alloys due to its hardness.
Q: Is TiNbZrSn suitable for biomedical implants?
A: Yes, it has been used for bone plates, hip and knee implants thanks to its biocompatibility, low modulus and high strength ideal for load-bearing devices. Grade 23 ELI powder provides the needed purity.
Q: What are typical applications for TiNbZrSn alloy?
A: Aerospace components like landing gear, automotive springs and fasteners, biomedical implants, armor plates, power generation turbines, and tooling for molding and sheet metal stamping.
Conclusion
In summary, TiNbZrSn alloy powder offers extraordinary strength coupled with low density, elasticity, and hardness unlike any other conventional or advanced alloys. Though costs are higher, many critical performance applications justify the expense where optimized material properties are paramount. With expanded availability and ongoing innovations, the unique capabilities of TiNbZrSn will be leveraged across more industries in the years ahead.
About Met3DP
Product Category
HOT SALE
CONTACT US
Any questions? Send us message now! We’ll serve your request with a whole team after receiving your message.