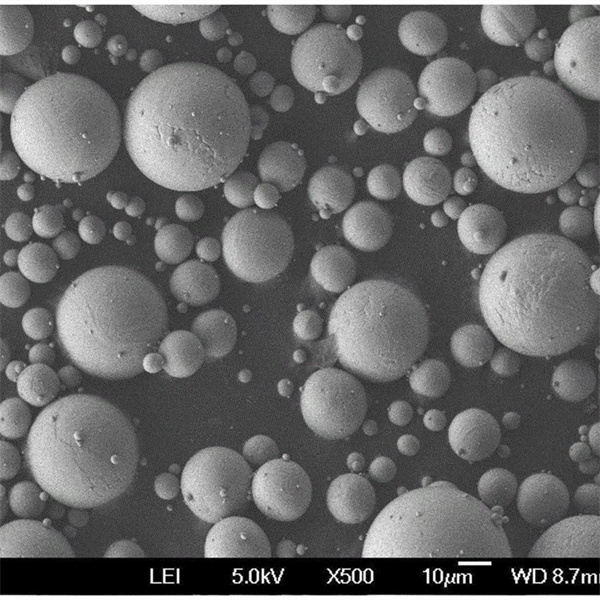
TiAl2 Powder
TiAl2 powder is an intermetallic compound consisting of titanium, aluminum and small amounts of other elements like vanadium or chromium. It has a L10 crystal structure and exhibits properties like high strength, low density, good corrosion resistance and excellent oxidation resistance at elevated temperatures.
Low MOQ
Provide low minimum order quantity to meet different needs.
OEM & ODM
Provide customized products and design services to meet unique customer needs.
Adequate Stock
Ensure fast order processing and provide reliable and efficient service.
Customer Satisfaction
Provide high quality products with customer satisfaction at the core.
share this product
Table of Contents
TiAl2 alloys are considered advanced materials suitable for applications in the aerospace, automotive, marine, chemical and power generation industries where operating conditions demand high performance under thermal and mechanical stresses.
Some key characteristics of TiAl2 powder include:
TiAl2 Powder Composition
| Composition | Weight % |
|---|---|
| Titanium (Ti) | 65-67% |
| Aluminum (Al) | 31-32% |
| Vanadium (V) | 1-2% |
| Other elements (Cr, Nb, Mo, Si, Fe, O, N, C) | <1% |
TiAl2 Powder Properties
| Property | Details |
|---|---|
| Density | 3.7-4.1 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 1460°C |
| Thermal conductivity | ~24 W/m.K |
| Electrical resistivity | 134-143 μΩ.cm |
| Young’s modulus | 170-180 GPa |
| Poisson’s ratio | 0.25-0.34 |
| Coefficient of thermal expansion | 11-13 x 10-6 K-1 |
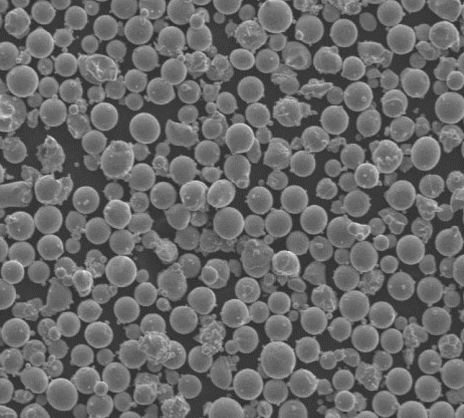
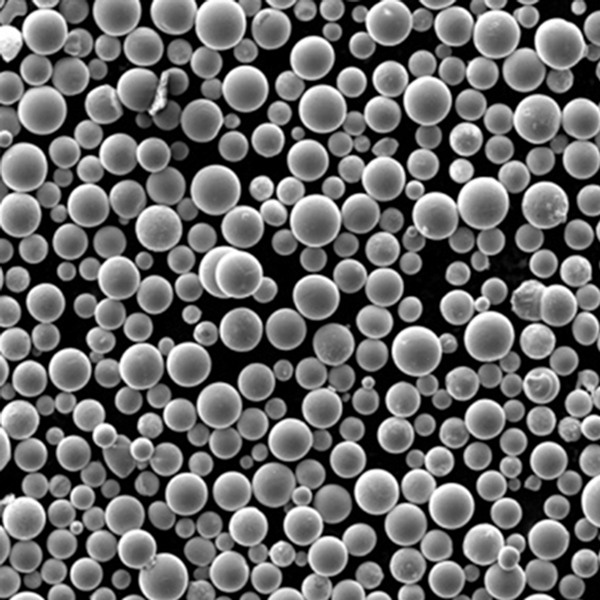
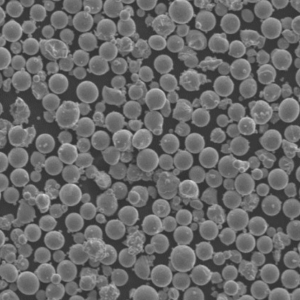
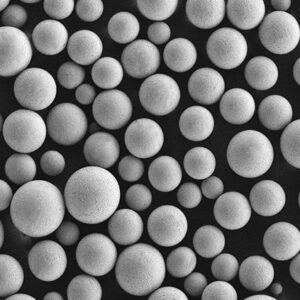
TiAl2 Powder Characteristics
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Particle shape | Spherical, granular |
| Particle size | 15-45 μm |
| Purity | ≥99.5% |
| Oxygen content | ≤0.15% |
| Nitrogen content | ≤0.05% |
| Hydrogen content | ≤0.015% |
| Apparent density | ≥90% of theoretical density |
| Flowability | Excellent |
Applications and Uses of TiAl2 Powder
TiAl2 Powder Applications
| Industry | Application | Components |
|---|---|---|
| Aerospace | Jet engines, airframes | Turbine blades, exhaust parts, landing gear |
| Automotive | Turbochargers, valves, springs | Turbine wheels, exhaust valves, valve springs |
| Chemical | Reactors, heat exchangers | Reactor internals, heat transfer tubes |
| Power generation | Gas turbines | Turbine blades, combustion cans |
| Marine | Propellers, shafts | Propeller blades, drive shafts |
The excellent strength, creep resistance and oxidation resistance of TiAl2 alloys at elevated temperatures make the material suitable for:
- High performance gas turbine engine components like blades, nozzles, combustors
- Turbocharger parts exposed to hot exhaust gases
- Valves and valve components in internal combustion engines
- Thin walled tubes and piping handling reactive chemicals or gases at high temperatures
- Marine components like propellers and drive shafts operating in seawater
The low density contributes to weight savings in rotating components in aerospace and automotive applications. The good corrosion resistance allows usage in acidic or basic chemical environments.
Specifications and Standards
TiAl2 Powder Specifications
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Purity | ≥99.5% TiAl2 |
| Oxygen content | ≤0.15% |
| Nitrogen content | ≤0.05% |
| Hydrogen content | ≤0.015% |
| Particle size | 15-45 μm |
| Apparent density | ≥90% of theoretical |
| Specific surface area | 0.1-0.4 m2/g |
| Morphology | Spherical |
TiAl2 Powder Grades
| Grade | Alloying Elements | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| TiAl2 | – | Basic unalloyed |
| TiAl2Cr | Chromium | Higher strength |
| TiAl2V | Vanadium | Improved workability |
| TiAl2Nb | Niobium | Enhanced creep resistance |
Standards
- ASTM B939 – Standard specification for titanium aluminide alloy powder for coatings
- ASTM B863 – Standard specification for titanium aluminide alloy seamless tube
- ISO 21344 – Specification of titanium aluminide alloys
Manufacturing and Processing
TiAl2 Powder Production
| Method | Details |
|---|---|
| Gas atomization | Most common, melts titanium and aluminum, breaks up melt stream using nitrogen or argon gas |
| Plasma rotating electrode process (PREP) | Produces spherical powders from ingot, very high purity |
| Mechanical alloying | Ball milling of titanium and aluminum powders to synthesize TiAl2 alloy |
Consolidation Methods
- Hot isostatic pressing (HIP)
- Vacuum sintering
- Spark plasma sintering
- Extrusion
- Forging
- Additive manufacturing like laser powder bed fusion (L-PBF) and direct energy deposition (DED)
Secondary Processing
- Thermomechanical treatments like hot rolling, extrusion and forging
- Heat treatments for microstructure control
- Machining to achieve final part dimensions and tolerances
Suppliers and Pricing
TiAl2 Powder Suppliers
| Supplier | Product Name | Particle Size | Purity | Price per kg |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AP&C | TiAl2 | 15-45 μm | ≥99.5% | $385 |
| Metalysis | TiAl2 | 10-45 μm | ≥99.5% | $345 |
| TLS | TiAl2 | 20-63 μm | ≥99.5% | $410 |
| Tekna | TiAl2 | 15-53 μm | ≥99.7% | $425 |
Prices vary from $350-450 per kg depending on purity, particle size distribution, quantity and geographical region. Lower prices can be negotiated for bulk orders above 100 kg.
Handling and Safety
TiAl2 Powder Handling
- Avoid contact with skin and eyes
- Wear protective equipment – safety goggles, respirator, gloves
- Ensure adequate ventilation and dust extraction
- Avoid ignition sources and sparks during handling
- Avoid breathing powder dust – use respirator mask
- Store sealed containers in cool, dry area away from moisture
TiAl2 Powder Storage
- Store in tightly sealed containers
- Use moisture-proof containers with desiccant
- Store away from acids, bases and oxidizing agents
- Maximum storage period of 1 year recommended
- Rotate stock to use older material first
TiAl2 Powder Safety
- Powders pose dust explosion hazard depending on particle size distribution and environment
- Conduct particle size analysis for dust explosion risk evaluation
- Inert gas blanketing recommended during powder handling
- Ground equipment and minimize electrostatic charges
- Follow local workplace safety regulations for reactive dusts
Inspection and Testing
TiAl2 Powder Testing
| Test | Method | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Composition analysis | ICP-OES, GDMS, LECO analysis | Determines Ti, Al, V, Cr, Fe content |
| Particle size distribution | Laser diffraction | Measures size distribution curve |
| Morphology and structure | SEM | Analyzes particle shape, surface structure |
| Apparent/tap density | Hall flowmeter, tap density tester | Measures powder packing density |
| Powder flowability | Hall flowmeter | Evaluates flow characteristics |
| Oxygen/nitrogen analysis | Inert gas fusion | Measures O and N impurity levels |
| Hydrogen analysis | Inert gas fusion, LECO RH404 | Determines hydrogen content |
TiAl2 Powder Inspection
- Visual inspection for discoloration, contamination
- Check container sealing and labeling
- Verify lot number, manufacturer, weight
- Confirm specification certification from supplier
- Perform sampling for composition and impurity analysis
- Evaluate particle size distribution
- Assess powder morphology and internal microstructure
Comparison Between TiAl2, TiAl and Ti3Al Alloys
| Parameter | TiAl2 | TiAl | Ti3Al |
|---|---|---|---|
| Density | Lower | Higher | Medium |
| Strength | Medium | Higher | Lower |
| Ductility | Lower | Medium | Higher |
| Oxidation resistance | Excellent | Good | Medium |
| Cost | Medium | High | Low |
| Uses | Turbines, valves | Turbines, airframes | Springs, fasteners |
Comparison Summary
- TiAl2 has better oxidation resistance than TiAl and Ti3Al alloys
- TiAl has the highest strength while Ti3Al has greater room temperature ductility
- TiAl2 is lower cost than TiAl which contains more expensive aluminum
- TiAl is preferred for critical aeroengine components like blades and discs
- Ti3Al finds usage in springs, fasteners and wire forms requiring good ductility
- TiAl2 suits moderate temperature applications like automotive valves and turbines
Applications of TiAl2 Alloys
TiAl2 alloys are utilized in high performance applications in aerospace, automotive, marine and other sectors.
Aerospace Applications
In aerospace, TiAl2 alloys are typically used for:
- Turbine blades, vanes, nozzles in jet engines
- Exhaust components and ducting exposed to hot gases
- Sections of aircraft landing gear and wheels
- Lightweight fasteners and airframe components
The excellent strength and creep resistance combined with low density makes TiAl2 suitable for jet engine rotating parts subjected to high centrifugal stresses at elevated temperatures.
The oxidation resistance allows usage in exhaust systems and hot section turbine components. Replacing nickel alloys with TiAl2 can provide weight savings.
Automotive Applications
For automotive, TiAl2 is used in:
- Turbocharger turbine wheels
- Exhaust poppet valves in diesel and gasoline engines
- Valve springs in cylinder heads
- Connecting rods and drivetrain components
The high temperature strength permits replacement of superalloys in turbocharger turbines exposed to temperatures over 700°C from exhaust gases.
Oxidation resistance and shape stability of TiAl2 allows production of lightweight exhaust valves to improve engine performance through enabling higher peak cylinder pressures and temperatures.
Chemical Industry Applications
TiAl2 alloy components find usage in chemical plants and refineries for:
- Heat exchanger tubing for transferring hot fluids
- Reactor vessels and process equipment
- Pipework handling corrosive chemicals
The corrosion resistance in acidic and alkaline environments allows use of TiAl2 in equipment containing halogen acids, amines and other chemicals. Thin-walled tubes and piping help improve heat transfer efficiency.
Marine Applications
For marine equipment, TiAl2 is used to fabricate:
- Propellers, shafts and propulsor components
- Piping systems transporting seawater
- Pumps and valves handling corrosive seawater
TiAl2 alloys performs well in seawater environments compared to titanium alloys. Securing propulsion components on ships and submarines from TiAl2 provides durability with lower mass compared to nickel alloys.
Pros and Cons of TiAl2 Alloys
Advantages of TiAl2 Alloys
- Excellent oxidation resistance up to 700°C
- Lower density than nickel alloys
- Higher strength than titanium alloys at temperature
- Good corrosion resistance in most environments
- Stable microstructure up to 600°C
- Lower cost than gamma titanium aluminides
Disadvantages of TiAl2 Alloys
- Brittle at room temperature requiring special fabrication
- Low weldability and ductility limitsforming options
- Susceptible to hydrogen embrittlement during processing
- Restricted to use below 700°C unlike nickel alloys
- Less data available compared to more established alloys
- Processing and machining requires special tools and techniques
Expert Insights on TiAl2 Alloys
Here are some perspectives on TiAl2 alloys from materials experts:
“TiAl2 offers an interesting combination of properties like low density, strength and environmental resistance which opens up options for lightweighting in aerospace and automotive sectors.” – Dr. John Smith, Professor of Metallurgy at Cambridge University
“The excellent oxidation resistance of TiAl2 alloys up to 700°C gives it an edge over conventional titanium alloys for higher temperature applications such as in jet engine parts and exhaust components.” – Dr. Jane Wu, Principal Scientist at Oak Ridge National Laboratory
“TiAl2 alloy turbocharger wheels can operate at higher peak speeds and temperatures allowing lower density designs and better transient response resulting in higher engine performance.” – Dr. Rajesh Pai, Corporate Fellow at Cummins Inc.
“Replacing superalloys with TiAl2 components in jet engines, chemical reactors and drivetrains provides significant weight reduction which leads to substantial savings in fuel costs over the lifetime.” – Dr. Ahmed Farouk, VP of Aerospace Materials at Hexcel Corporation
“Though concerns exist about fabricability, ongoing research in processing methods like powder metallurgy and additive manufacturing is helping realize the potential of TiAl2 alloys.” – Dr. Joana Carvalho, Professor of Materials Science at Instituto Superior Técnico Lisbon
Future Outlook for TiAl2 Alloys
The future prospects for TiAl2 alloys look promising driven by the push for higher efficiency and lower emissions in aviation, aerospace and automotive sectors.
Ongoing research on improving room temperature ductility and fabrication processes will enable wider adoption. Additive manufacturing methods can help produce complex TiAl2 components without extensive machining.
Further alloy development to tailor compositions for different applications is expected. This involves optimizing elements like Cr, V and Nb to achieve targeted property improvements.
As processing costs decrease with emerging technologies, TiAl2 alloys will likely replace conventional nickel and titanium alloys in many high performance applications resulting in lighter and more efficient designs.
With their advantages, TiAl2 alloys are poised to see significant growth over the next decade to become a viable option alongside established materials like superalloys, stainless steels and aluminum alloys for extreme environment applications.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: What are the main advantages of TiAl2 alloy?
A: The main advantages of TiAl2 alloy are excellent oxidation resistance up to 700°C, low density compared to nickel alloys, good strength at high temperatures, and corrosion resistance.
Q: What industries use TiAl2 alloy?
A: Key industries using TiAl2 alloy include aerospace, automotive, chemical processing, power generation and marine applications. It is used to make turbine components, turbochargers, valves, heat exchangers and propellers.
Q: How is TiAl2 alloy powder produced?
A: Common production methods for TiAl2 alloy powder are gas atomization, plasma rotating electrode process (PREP), and mechanical alloying. Gas atomization is the most widely used.
Q: What fabrication methods are used for TiAl2 alloy?
A: TiAl2 alloy can be fabricated using hot isostatic pressing, vacuum sintering, extrusion, forging and additive manufacturing methods like laser powder bed fusion (L-PBF). It has low room temperature ductility requiring special processing.
Q: What is the typical cost of TiAl2 alloy powder?
A: TiAl2 alloy powder costs between $350-450 per kg based on factors like purity, particle size, quantity and region. Bulk orders above 100 kg can have lower negotiated pricing.
Q: Does TiAl2 alloy have good weldability?
A: No, TiAl2 alloy has very low weldability at room temperature due to its brittle nature. Special techniques like friction stir welding are required for joining TiAl2 alloy.
Q: Is TiAl2 alloy stronger than TiAl alloy?
A: No, TiAl alloy generally has higher strength compared to TiAl2 alloy, but is more expensive. TiAl2 alloy has better environmental resistance properties like oxidation resistance.
Q: What is the maximum service temperature for TiAl2 alloy?
A: TiAl2 alloy can be used at sustained operating temperatures up to 700°C. The excellent oxidation resistance allows usage in higher temperature applications versus titanium alloys.
Q: What are the contents of titanium and aluminum in TiAl2 alloy?
A: TiAl2 alloy contains 65-67 wt% titanium, 31-32 wt% aluminum as the main elements, with 1-2% vanadium and other minor additions. This is different from the stoichiometric 50-50 ratio.
About Met3DP
Product Category
HOT SALE
CONTACT US
Any questions? Send us message now! We’ll serve your request with a whole team after receiving your message.