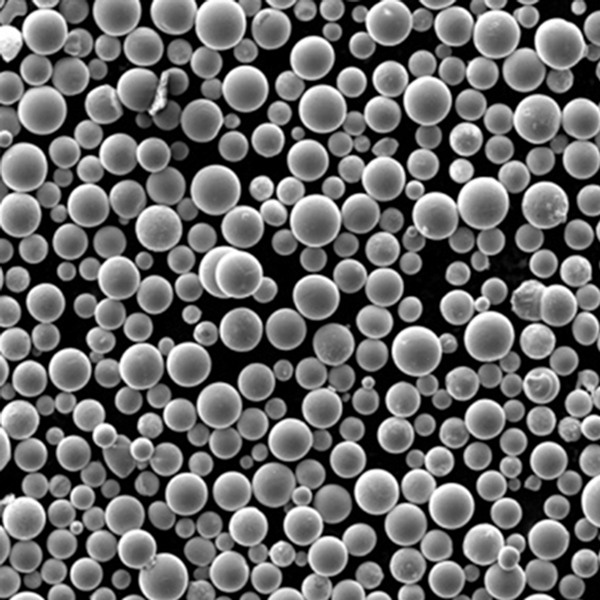
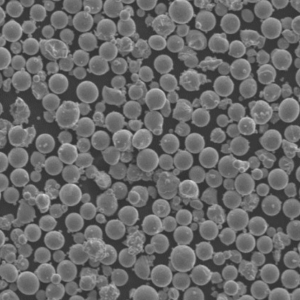
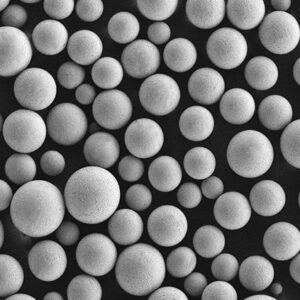
CuSn10 Powder
CuSn10 powder is a copper-tin alloy containing approximately 10% tin and the remainder copper. It offers an excellent combination of strength, ductility, corrosion resistance, wear resistance, and antifriction properties.
Low MOQ
Provide low minimum order quantity to meet different needs.
OEM & ODM
Provide customized products and design services to meet unique customer needs.
Adequate Stock
Ensure fast order processing and provide reliable and efficient service.
Customer Satisfaction
Provide high quality products with customer satisfaction at the core.
share this product
Table of Contents
Overview of CuSn10 Powder
CuSn10 powder is a copper-tin alloy containing approximately 10% tin and the remainder copper. It offers an excellent combination of strength, ductility, corrosion resistance, wear resistance, and antifriction properties.
Key properties and applications of CuSn10 powder include:
CuSn10 Powder Properties and Characteristics
| Properties | Details |
|---|---|
| Composition | 90% copper, 10% tin |
| Density | 8.8 g/cc |
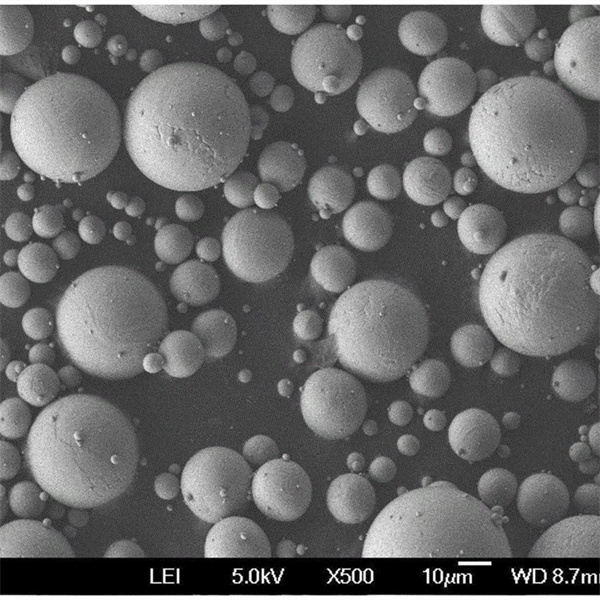
| Particle shape | Irregular, angular |
| Size range | 5-150 microns |
| Apparent density | Up to 50% of true density |
| Flowability | Moderate |
| Strength | Excellent for Cu alloy powder |
| Ductility | Good |
| Corrosion resistance | Very good |
CuSn10 is widely used in bearing cages, bushings, welding rods, and wear parts across the automotive, electrical, and industrial sectors.
CuSn10 Powder Composition
Typical composition of CuSn10 powder:
CuSn10 Powder Composition
| Element | Weight % |
|---|---|
| Copper (Cu) | Remainder |
| Tin (Sn) | 9-11% |
| Lead (Pb) | 0.2% max |
| Zinc (Zn) | 0.5% max |
| Other impurities | 0.1% max |
- Copper provides excellent conductivity, corrosion resistance, ductility
- Tin improves strength, hardness, and wear resistance
- Lead, zinc, and other impurities carefully controlled
The optimized Cu-Sn ratio provides an excellent combination of strength, ductility, and manufacturability.
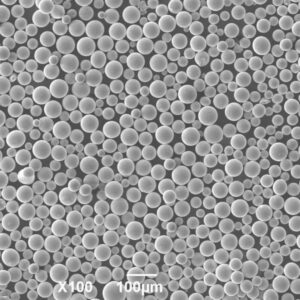
CuSn10 Powder Physical Properties
CuSn10 Powder Physical Properties
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Density | 8.8 g/cc |
| Melting point | 1020-1040°C |
| Thermal conductivity | 55 W/mK |
| Electrical resistivity | 7-9 μΩ-cm |
| Recrystallization temperature | 150-250°C |
| Maximum service temperature | 250°C |
- Density is higher than copper
- Melting point reduced compared to pure copper
- Maintains good conductivity
- Recrystallization enables powder compaction
- Can withstand moderately high operating temperatures
The physical properties allow use of CuSn10 in electrical components needing good conductivity and strength.
CuSn10 Powder Mechanical Properties
CuSn10 Powder Mechanical Properties
| Property | Values |
|---|---|
| Hardness | 80-110 HB |
| Tensile strength | 350-550 MPa |
| Yield strength | 220-320 MPa |
| Elongation | 10-20% |
| Modulus of elasticity | 110-140 GPa |
- Excellent strength for a copper alloy powder
- Significantly higher than pure copper powder
- Good ductility for 10% tin composition
- Hardness values suitable for wear applications
- Properties depend on production method and porosity
The mechanical properties allow use of CuSn10 powder in high strength electrical and friction components.
CuSn10 Powder Applications
Typical applications of CuSn10 powder include:
CuSn10 Powder Applications
| Industry | Application Examples |
|---|---|
| Automotive | Bearings, bushings, brake linings |
| Electrical | Welding electrodes, connectors, contacts |
| Industrial | Bearing cages, seals, impellers |
| Manufacturing | Sintered tooling components |
| Oil and gas | Bushings, ball valves |
Some specific product uses:
- Bearing cages requiring antifriction properties
- Bushing and thrust washers in high load applications
- Automotive brake pads and clutch linings
- Electrical connectors and pins
- Welding rods and solder paste filler metal
- Piping components like valves and flanges
Its excellent combination of strength, ductility, and cost make CuSn10 a popular choice for these applications.
CuSn10 Powder Specifications
The main specifications for CuSn10 powder include:
CuSn10 Powder Specifications
| Standard | Description |
|---|---|
| ISO 44001 | Copper and copper alloy powders – Specifications |
| ASTM B602 | Standard specification for copper alloy powders |
| EN 1982 | Specification for copper and copper alloys ingots and castings |
| JIS H2111 | Bronze powders |
These define:
- Chemical composition limits
- Production method – atomization
- Required physical and mechanical properties
- Acceptable impurity levels
- Particle size distribution
- Testing protocols
Compliance ensures suitability for intended applications across global markets.
CuSn10 Powder Particle Sizes
CuSn10 Powder Particle Size Distribution
| Particle Size | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| 5-25 microns | Ultrafine grade for high density and surface finish |
| 15-45 microns | Common size for pressing and sintering |
| 45-150 microns | Larger sizes for better powder flowability |
- Finer particles allow greater densification
- Larger particles improve powder flow properties
- Size is selected based on final part properties needed
- Both spherical and irregular shapes are available
Controlling particle size distribution optimizes pressing characteristics and final sintered density.
CuSn10 Powder Apparent Density
CuSn10 Powder Apparent Density
| Apparent density | Details |
|---|---|
| Up to 50% of true density | For irregular morphology powder |
| 4.5-6.5 g/cc | Improves with greater packing density |
- Higher apparent density improves powder flow and compactibility
- Density up to 60% is possible with optimized spherical powder
- High apparent density enables easier compaction into green parts
Higher apparent density leads to better manufacturing productivity and part quality.
CuSn10 Powder Production Method
CuSn10 Powder Production
| Method | Details |
|---|---|
| Atomization | Melted alloy stream broken into fine droplets which solidify into powder |
| Induction melting | Pure copper and tin melted together under controlled atmosphere |
| Inert gas atomization | Prevent oxidation of particles during production |
| Sieving | Classifies powder into different particle size ranges |
- Automated atomization enables large scale production
- Controlled melting and atomization minimizes impurities
- Inert gas prevents powder oxidation
- Post-processing allows customization of particle sizes
Strict process controls result in reliable powder quality and repeatable characteristics.
CuSn10 Powder Pricing
CuSn10 Powder Pricing
| Factor | Impact on Price |
|---|---|
| Purity grade | Higher purity increases price |
| Particle size | Finer powder is more expensive |
| Order quantity | Bulk pricing discounts apply |
| Production method | Complex processes increase cost |
| Additional services | Customization adds cost |
Indicative Pricing
- CuSn10 powder: $8-12 per kg
- Lower prices applicable for bulk orders >1000 kg
Pricing varies based on order parameters like quantity, particle size, purity level, alloy composition etc.
CuSn10 Powder Suppliers
CuSn10 Powder Suppliers
| Company | Location |
|---|---|
| Kymera International | USA |
| Hoganas | Sweden |
| CNPC Powder Group | China |
| Shanghai CNPC Powder Material | China |
| Gujarat Reclaim Industries | India |
| American Chemet Corporation | USA |
Selection factors for suppliers:
- Powder sizes and lead time
- Customization capability
- Production capacity
- Packaging options
- Pricing levels
- Quality certifications and compliance
CuSn10 Powder Handling and Storage
CuSn10 Powder Handling
| Recommendation | Reason |
|---|---|
| Avoid inhalation | Potential respiratory irritation |
| Use protective mask and goggles | Prevent accidental ingestion |
| Ensure adequate ventilation | Reduce airborne particles |
| Avoid ignition sources | Flammable dust hazard |
| Follow anti-static procedures | Prevent fire from static discharge |
| Use non-sparking tools | Avoids sparks during handling |
| Store sealed containers in cool, dry area | Prevent oxidation and moisture absorption |
Storage Recommendations
- Store in stable, inert containers
- Keep away from acids, ammonia, acetylene
- Maintain temperatures below 27°C
Proper handling and storage preserves powder purity and prevents reaction hazards.
CuSn10 Powder Inspection and Testing
CuSn10 Powder Testing
| Test | Details |
|---|---|
| Chemical analysis | ICP and XRF to verify composition |
| Particle size distribution | Sieve analysis or laser diffraction |
| Apparent density | Hall flowmeter test per ASTM B212 |
| Powder morphology | SEM imaging of particle shape |
| Tap density | Density measured after mechanical tapping |
| Flow rate analysis | Gravity flow rate through specified nozzle |
Stringent testing ensures the powder meets the chemical composition, physical properties, and microstructure required for the application.
CuSn10 Powder Pros and Cons
Advantages of CuSn10 Powder
- Excellent strength for a copper alloy powder
- Good ductility and formability
- Very good corrosion resistance
- Cost-effective compared to bronze grades
- Good electrical and thermal conductivity
- Recyclable and environmentally friendly
Disadvantages of CuSn10 Powder
- Lower conductivity than pure copper powder
- Moderate high temperature strength
- Heavy compared to aluminum or magnesium alloys
- Not suitable for highly stressed structural components
- Surface discoloration over time if uncoated
- Limitations for food contact applications
Comparison With CuNi10 Powder
CuSn10 vs CuNi10 Powder
| Parameter | CuSn10 | CuNi10 |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 8.8 g/cc | 8.9 g/cc |
| Strength | 350-550 MPa | 500-650 MPa |
| Conductivity | 55 W/mK | 20 W/mK |
| Corrosion resistance | Excellent | Very Good |
| Cost | Low | High |
| Uses | Electrical, moderate load | High strength structures |
- CuSn10 provides better conductivity and cost
- CuNi10 has higher tensile strength
- CuSn10 preferred for electrical components
- CuNi10 suited for high strength structural parts
CuSn10 Powder FAQs
Q: What are the main applications of CuSn10 powder?
A: Main applications include bearing cages, bushings, welding rods, brake linings, antifriction components, and electrical contacts, connectors and brushes. It is commonly used in automotive and electrical products.
Q: Does CuSn10 powder require special handling precautions?
A: General precautions are recommended including avoiding inhalation, ensuring proper ventilation, controlling dust, preventing ignition sources, avoiding static charge buildup, using non-sparking tools, and storing in a dry, inert atmosphere.
Q: What affects the properties of CuSn10 powder parts?
A: Key factors are apparent density, particle size distribution, compaction pressure, sintering temperature and time, alloy composition, impurities, and porosity.
Q: What is the key difference between bronze and CuSn10 powders?
A: Bronze powders contain 90-95% copper while CuSn10 has 90% copper, 10% tin. CuSn10 provides an optimal combination of strength, ductility and cost.
About Met3DP
Product Category
HOT SALE
CONTACT US
Any questions? Send us message now! We’ll serve your request with a whole team after receiving your message.