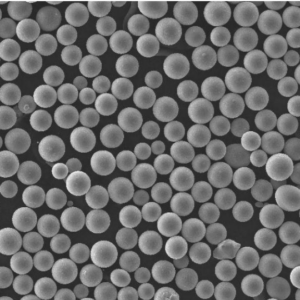
310 Powder
310 powder is an austenitic stainless steel powder containing high levels of chromium, nickel and nitrogen for enhanced mechanical properties and corrosion resistance. It offers an excellent combination of strength, hardness, toughness and wear resistance.
Low MOQ
Provide low minimum order quantity to meet different needs.
OEM & ODM
Provide customized products and design services to meet unique customer needs.
Adequate Stock
Ensure fast order processing and provide reliable and efficient service.
Customer Satisfaction
Provide high quality products with customer satisfaction at the core.
share this product
Table of Contents
Overview of 310 Powder
310 powder is an austenitic stainless steel powder containing high levels of chromium, nickel and nitrogen for enhanced mechanical properties and corrosion resistance. It offers an excellent combination of strength, hardness, toughness and wear resistance.
Key properties and advantages of 310 powder include:
310 Powder Properties and Characteristics
| Properties | Details |
|---|---|
| Composition | Fe-25Cr-20Ni-0.25N alloy |
| Density | 8.1 g/cc |
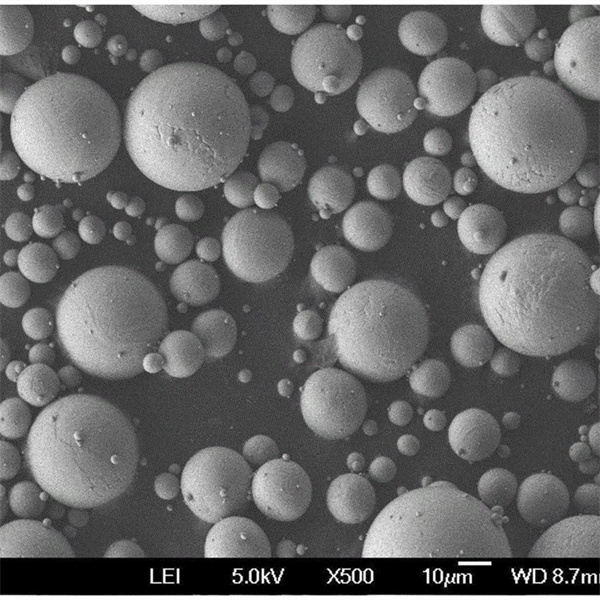
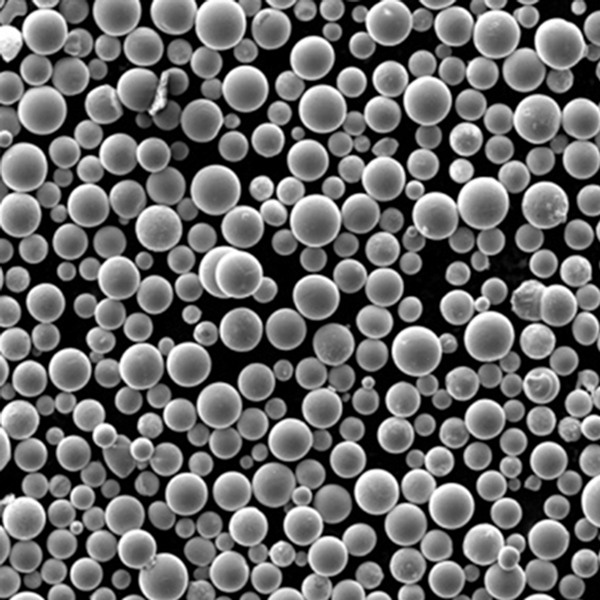
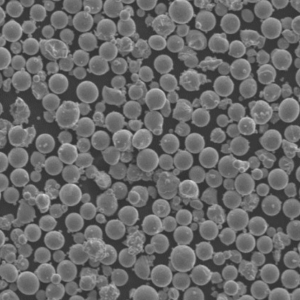
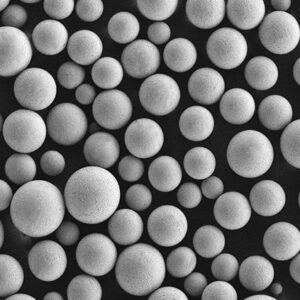
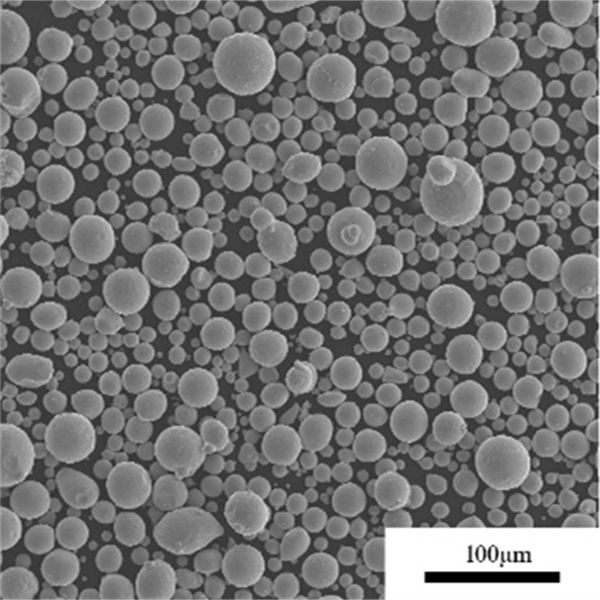
| Particle shape | Irregular, angular |
| Size range | 10-150 microns |
| Apparent density | Up to 50% of true density |
| Flowability | Moderate |
| Strength | Very high for a 300 series powder |
| Wear resistance | Excellent due to work hardening |
310 powder is widely used in applications requiring hardness, wear resistance, and corrosion resistance like valve parts, shafts, bearing cages, fasteners, surgical instruments etc.
310 Powder Composition
Typical composition of 310 stainless steel powder:
310 Powder Composition
| Element | Weight % |
|---|---|
| Iron (Fe) | Balance |
| Chromium (Cr) | 24-26% |
| Nickel (Ni) | 19-22% |
| Nitrogen (N) | 0.2-0.4% |
| Carbon (C) | 0.25% max |
| Silicon (Si) | 1.5% max |
| Manganese (Mn) | 2% max |
| Sulfur (S) | 0.03% max |
| Phosphorus (P) | 0.045% max |
- Iron provides the ferritic matrix and ductility
- Chromium and nickel enhance corrosion resistance
- Nitrogen provides solid solution strengthening
- Carbon, silicon, manganese controlled as tramp elements
The optimized composition provides an excellent combination of strength, hardness, corrosion resistance, and cost.
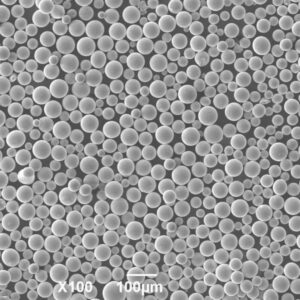
310 Powder Physical Properties
310 Powder Physical Properties
| Property | Values |
|---|---|
| Density | 8.1 g/cc |
| Melting point | 1370-1400°C |
| Electrical resistivity | 0.8 μΩ-m |
| Thermal conductivity | 12 W/mK |
| Thermal expansion | 11 x 10^-6 /K |
| Maximum service temperature | 1150°C |
- High density compared to ferritic stainless steels
- Maintains excellent strength at elevated temperatures
- Resistivity higher than pure iron or carbon steels
- Lower thermal conductivity than carbon steel
- Can withstand continuous service up to 1150°C
The physical properties make 310 suitable for high temperature applications requiring hardness, strength and corrosion resistance.
310 Powder Mechanical Properties
310 Powder Mechanical Properties
| Property | Values |
|---|---|
| Tensile strength | 760-900 MPa |
| Yield strength | 450-550 MPa |
| Elongation | 35-40% |
| Hardness | 32-38 HRC |
| Impact strength | 50-100 J |
| Modulus of elasticity | 190-210 GPa |
- Very high strength for 300 series stainless steel
- Excellent hardness and wear resistance
- High toughness and impact strength
- Strength can be further increased through cold working
- Cold working also significantly enhances hardness
The properties provide an excellent combination of strength, hardness and toughness required in many wear resistant applications.
310 Powder Applications
Typical applications of 310 stainless steel powder include:
310 Powder Applications
| Industry | Example Uses |
|---|---|
| Petrochemical | Valves, pumps, shafts |
| Food processing | Extruder screws, blades |
| Automotive | Gears, shafts, fasteners |
| Manufacturing | Press tooling, bearing cages |
| Medical | Surgical instruments, implants |
Some specific product uses:
- High strength fasteners, bolts, nuts
- Pump and valve components like seals, shafts
- Food processing extruder screws and blades
- High hardness press tooling and molds
- Mixing equipment, impellers requiring wear resistance
Its excellent combination of properties make 310 widely used for specialized applications across industries.
310 Powder Specifications
Relevant specifications and standards:
310 Powder Standards
| Standard | Description |
|---|---|
| ASTM A276 | Standard specification for stainless steel bars and shapes |
| ASTM A314 | Standard for stainless steel bent pipe and tubing |
| ASME SA-479 | Specification for stainless steel tubing |
| AMS 5517 | Annealed corrosion resistant steel bar, wire, forgings |
| AMS 5903 | Precipitation hardening stainless steel bar, wire, forgings |
These standards define:
- Chemical composition limits of 310 alloy
- Permissible impurity levels like S, P
- Required mechanical properties
- Approved production methods
- Compliance testing protocols
- Proper packaging, labeling and documentation
Meeting certification requirements ensures suitability of the powder.
310 Powder Particle Sizes
310 Powder Particle Size Distribution
| Particle Size | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| 10-45 microns | Ultrafine grade for high density and surface finish |
| 45-150 microns | Coarse grade provides good flowability |
| 15-150 microns | Standard grade for pressing and sintering |
- Finer particles allow greater densification during sintering
- Coarser powder flows better and fills die cavities uniformly
- Size range is tailored based on final part properties needed
- Both gas and water atomized powders are available
Controlling particle size distribution allows optimizing processing behavior and final part performance.
310 Powder Apparent Density
310 Powder Apparent Density
| Apparent Density | Details |
|---|---|
| Up to 50% of true density | For irregular powder morphology |
| 4.5-5.5 g/cc typical | Improves with greater packing density |
- Higher apparent density improves powder flow and compressibility
- Irregular morphology limits maximum packing density
- Values up to 60% are possible with spherical powders
- High apparent density improves press filling efficiency
Higher apparent density leads to better manufacturing productivity and part quality.
310 Powder Production Method
310 Powder Production
| Method | Details |
|---|---|
| Gas atomization | High pressure inert gas breaks molten metal stream into fine droplets |
| Water atomization | High pressure water jet breaks metal into fine particles |
| Vacuum induction melting | High purity input materials melted under vacuum |
| Multiple remelting | Improves chemical homogenization |
| Sieving | Classifies powder into different particle size ranges |
- Gas atomization provides clean, spherical powder morphology
- Water atomization is a lower cost process with irregular particles
- Vacuum melting and remelting minimizes gaseous impurities
- Post-processing allows customization of particle sizes
Automated production and stringent quality control result in consistent powder suitable for critical applications.
310 Powder Pricing
310 Powder Pricing
| Factor | Impact on Price |
|---|---|
| Purity level | Higher purity increases cost |
| Powder morphology | Spherical powder costs more |
| Particle size | Ultrafine powder more expensive |
| Order volume | Larger quantities have lower per unit pricing |
| Additional services | Customization adds cost |
Indicative Pricing
- Irregular 310 powder: $8-12 per kg
- Spherical 310 powder: $12-18 per kg
- Large volume pricing can be 30-50% lower
Pricing depends on purity, particle characteristics, order volume, and customization needs.
310 Powder Suppliers
310 Powder Suppliers
| Company | Location |
|---|---|
| Höganäs | Sweden |
| Sandvik | Germany |
| Daido Steel | Japan |
| CNPC Powder | China |
| Carpenter Powder Products | USA |
| Erasteel | France |
Key supplier selection factors:
- Powder grades offered
- Production capacity
- Particle morphology and size ranges
- Batch analysis reports
- Pricing and minimum order quantity
- Customization services
- Delivery times and reliability
310 Powder Handling and Storage
310 Powder Handling
| Recommendation | Reason |
|---|---|
| Use PPE and ventilation | Avoid exposure to fine metallic particles |
| Ensure proper grounding | Prevent static discharge while handling |
| Avoid ignition sources | Powder can combust in oxygen atmosphere |
| Use non-sparking tools | Prevent possibility of ignition |
| Follow safety protocols | Reduce risk of burns, inhalation, ingestion |
| Store in stable containers | Prevent contamination or oxidation |
As 310 powder is flammable, ignition and explosion risks should be controlled during handling and storage. Otherwise it is relatively safe with proper precautions.
310 Powder Inspection and Testing
310 Powder Testing
| Test | Details |
|---|---|
| Chemical analysis | ICP and XRF verify composition |
| Particle size distribution | Laser diffraction determines size distribution |
| Apparent density | Hall flowmeter test per ASTM B212 standard |
| Powder morphology | SEM imaging shows particle shape |
| Flow rate analysis | Gravity flow rate through specified nozzle |
| Loss on ignition | Determines residual moisture content |
Stringent testing ensures the powder meets the required chemical purity, particle characteristics, density, morphology, and flowability per applicable specifications.
310 Powder Pros and Cons
Advantages of 310 Powder
- Excellent strength and hardness for stainless steel powder
- High temperature strength and corrosion resistance
- Good ductility, toughness and weldability
- Excellent wear and abrasion resistance
- Readily work hardens significantly
- More cost-effective than high nickel or exotic alloys
Disadvantages of 310 Powder
- Lower ductility than austenitic grades in annealed state
- Lower pitting corrosion resistance than 316 grade
- Requires care during welding to avoid sensitization
- Limited cold heading and forming capability
- Susceptible to sigma phase embrittlement at high temperatures
- Surface discoloration over time in some environments
Comparison With 316L Powder
310 vs 316L Stainless Steel Powder
| Parameter | 310 | 316L |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 8.1 g/cc | 8.0 g/cc |
| Strength | 760-900 MPa | 485-550 MPa |
| Hardness | 32-38 HRC | 79-95 HRB |
| Corrosion resistance | Very good | Excellent |
| Cost | Low | High |
| Uses | Wear parts, tools | Chemical plants, marine |
- 310 has far higher strength and hardness
- 316L provides better overall corrosion resistance
- 310 is more cost-effective than 316L
- 310 suited for applications needing hardness and wear resistance
- 316L preferred where corrosion is the primary concern
310 Powder FAQs
Q: What are the main applications of 310 stainless steel powder?
A: Main applications include high-strength fasteners, pump and valve components, extruder screws, press tooling, bearing cages, shafts, and surgical instruments requiring hardness, strength and wear resistance.
Q: What is nitrogen’s role in 310 stainless steel?
A: Nitrogen provides substantial solid solution strengthening which significantly increases the strength and hardness of 310 stainless steel.
Q: What precautions are needed when working with 310 powder?
A: Recommended precautions include ventilation, inert atmosphere, grounding, avoiding ignition sources, protective gear, using non-sparking tools, and safe storage in stable containers.
Q: How does 310 stainless steel differ from 304 and 316 grades?
A: 310 has much higher strength and hardness than 304 or 316 due to its high nitrogen content. It offers better wear resistance but lower corrosion resistance than 316.
About Met3DP
Product Category
HOT SALE
CONTACT US
Any questions? Send us message now! We’ll serve your request with a whole team after receiving your message.