Inconel powder refers to a family of nickel-chromium-based superalloys with excellent high temperature strength, corrosion resistance, and oxidation resistance properties. This guide provides a detailed overview of inconel powder including types, characteristics, applications, specifications, suppliers, installation, operation and maintenance procedures, selection criteria, pros and cons, and FAQs.
Overview of Inconel Powder
Inconel is a registered trademark referring to a variety of precipitation-hardened nickel-based superalloys containing nickel, chromium, and other alloying elements like iron, niobium, aluminum, titanium, etc.
Key properties of inconel powder:
- High temperature strength and creep resistance
- Excellent corrosion resistance
- Good oxidation and carburization resistance
- High fatigue strength and toughness
- Resistant to chlorine and fluorine compounds
- Non-magnetic
Inconel powder is widely used in applications requiring heat resistance like gas turbines, rocket motors, nuclear reactors, and chemical processing equipment. Common inconel alloys include Inconel 600, Inconel 625, Inconel 718, Inconel X-750, etc.
Types of Inconel Powder
There are several varieties of inconel powder designed for specific applications and requirements:
| Types | Composition | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Inconel 600 | 72% Ni, 16% Cr | Excellent corrosion resistance |
| Inconel 625 | 60% Ni, 20-23% Cr, 8-10% Fe | Oxidation and corrosion resistance up to 980°C |
| Inconel 718 | 50-55% Ni, 17-21% Cr, 4.75-5.5% Nb | Age hardenable, high tensile and creep rupture strength |
| Inconel X-750 | 72% Ni, 15% Cr, 7% Fe | Precipitation hardening alloy, oxidation resistance |
| Inconel MA 6000 | 65% Ni, 10% Cr, 5% Al | Oxidation resistance, used in glass molds |
| Inconel MA 754 | 79% Ni, 14.5% Cr, 2.5% Ti, 1.5% Al | High creep strength up to 1150°C |
| Inconel MA 6000E | 63% Ni, 8% Cr, 4% Al, 0.5% Y2O3 | Enhanced oxidation resistance |
The specific inconel powder is selected based on required properties, maximum operating temperature, corrosion resistance needs, etc.
Applications and Uses of Inconel Powder
Inconel powder is suitable for a wide range of applications:
| Industry | Applications |
|---|---|
| Aerospace | Gas turbine engines, rocket motors, exhaust systems |
| Oil and gas | Drilling equipment, offshore platforms, valves and piping |
| Power generation | Gas turbines, nuclear reactors, heat exchangers |
| Chemical processing | Reactors, heaters, crackers, vessels, pipes |
| Automotive | Valves, exhaust and turbocharger parts |
| Pollution control | Scrubbers, chimneys, incinerators |
| Glass industry | Glass molds, stirrers, plungers |
Some key usage benefits:
- High temperature strength for better efficiency
- Corrosion resistance for long service life
- Oxidation resistance under extreme environments
- Dimensional stability at elevated temperatures
- High fatigue strength for dynamic applications
Specifications of Inconel Powder
Inconel powder is available with various characteristics:
| Specifications | Details |
|---|---|
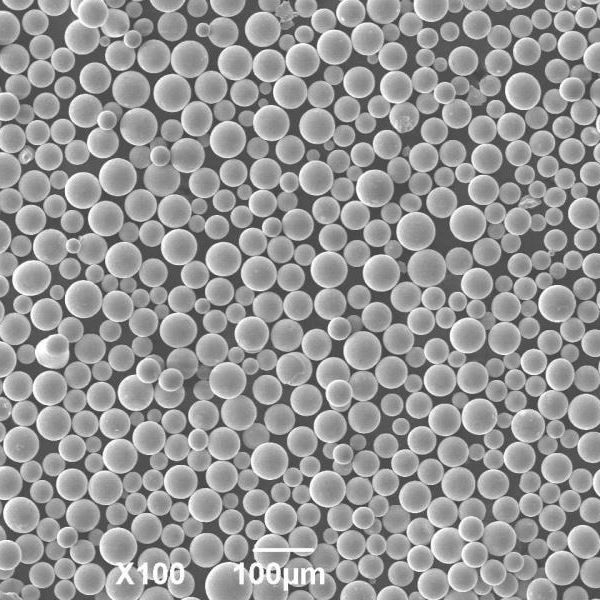
| Particle size | 10 – 150 microns |
| Particle shape | Spherical, irregular |
| Production method | Gas atomization, water atomization |
| Apparent density | 2 – 5 g/cc |
| Tap density | Up to 60% of theoretical density |
| Flow rate | 5 – 25 s/50g |
| Purity | ASTM grades (B,C,D), custom alloys |
| Composition | Nickel + chromium + alloying elements |
It can be customized in terms of:
- Alloy composition and microstructure as per requirement
- Particle size distribution suitable for application method
- Shape and flow characteristics
- Required density and porosity
- Certification as per application standards
Suppliers and Pricing of Inconel Powder
Some of the major global inconel powder suppliers include:
| Company | Location | Price Range |
|---|---|---|
| Sandvik | Sweden | $50 – $120 per kg |
| Praxair | USA | $55 – $140 per kg |
| TLS Technik | Germany | $60 – $150 per kg |
| Japan New Metals Co | Japan | $70 – $180 per kg |
| Nanoshel | USA | $45 – $100 per kg |
Prices depend on:
- Alloy grade and purity
- Particle size range and distribution
- Volume of order
- Additional treatment or characterization
Customization available at premium pricing. Discounts can be negotiated on bulk orders.
Installation of Inconel Powder System
Key considerations for installing inconel powder handling systems:
| Parameter | Guidelines |
|---|---|
| Storage | Inert gas environment, temperature control |
| Handling | Minimize exposure to air, safety equipment |
| Transfer lines | Leak-proof, minimize dead zones |
| Grounding | Avoid static charge buildup |
| Safety systems | Inert gas, fire detection, explosion venting |
| Design | Enclose critical sections, ease of maintenance |
| Materials | Compatible with inconel powder, minimize reactions |
Critical factors:
- Prevent oxygen content exceeding explosive limits
- Proper grounding and bonding to avoid sparks
- Leak-proof transferring and metering provisions
- Ventilation and safety monitoring systems
- Accessibility for inspection and maintenance
Operation and Maintenance of Inconel Powder Equipment
| Activity | Guidelines |
|---|---|
| Filling | Controlled inert gas purging, verify seals post-filling |
| Operation | Follow SOPs, monitor parameters like pressure and temperature |
| Inspection | Check for clogging, leakage, wear and powder quality |
| Maintenance | Replace worn parts, seals, leak testing, calibration |
| Safety | Ensure continuous inert gas supply, grounding, PPE |
| Cleanup | Careful vacuum cleaning to collect spilled powder |
Key operation protocols:
- Maintain oxygen levels below 5%
- Prevent accumulation of powder deposits
- Monitor flow rates, density, pressure drops
- Frequently inspect for blocked lines, leaks
- Verify continuous grounding and inert gas system
- Ensure safe powder disposal and reuse
Choosing an Inconel Powder Supplier
Factors to consider when selecting an inconel powder supplier:
| Criteria | Considerations |
|---|---|
| Powder quality | Composition, particle size, microstructure |
| Technical expertise | Alloy knowledge, customization capability |
| Manufacturing process | Gas atomization preferred |
| Certifications | ISO, industry standards like AMS |
| R&D capabilities | Expertise in developing custom alloys |
| Delivery | On-time delivery record |
| Pricing | Competitive pricing, discounts |
| Customer service | Technical support, responsiveness |
Key steps:
- Review alloy composition reports from independent testing
- Validate manufacturing process and quality certifications
- Assess ability to customize alloys and particle characteristics
- Evaluate technical competence and customer service level
- Audit supplier’s quality management system
- Sample evaluation trials before large volume procurement

Pros and Cons of Inconel Powder
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Excellent high temperature properties | Expensive compared to steel |
| Corrosion resistance in wide range of media | Lower thermal conductivity than copper alloys |
| High fatigue strength | Reactive with oxygen at high temperatures |
| Good oxidation resistance up to 1000°C | Susceptible to sulfur embrittlement |
| High creep rupture strength | Difficult to machine and fabricate |
| Non-magnetic property | Limited suppliers and availability |
Ideal for critical applications needing temperature resistance despite higher cost. Limitations in thermal conductivity, machinability, availability, and cost restrict more widespread use.
FAQs
Q: What are the main alloying elements in inconel powder?
A: The main alloying elements are chromium, iron, niobium, titanium, aluminum, and molybdenum added to nickel. These enhance high temperature strength, corrosion resistance, and age hardening response.
Q: What particle size range is commonly used for inconel powder in AM?
A: For additive manufacturing, inconel powder with particle size between 15-45 microns is typically used. Finer powder below 100 microns improves sintering and performance.
Q: What safety precautions are important when handling inconel powder?
A: Avoid contact with air using inert gas blanketing, ground all equipment properly, employ spark detection and fire suppression systems, use PPE, and follow protocols to prevent explosion risks.
Q: What are the typical applications of Inconel 718 powder?
A: Inconel 718 is widely used in aircraft engines, rockets, nuclear reactors, pumps, and cryogenic tankage due to its high strength at elevated temperatures and good corrosion resistance.
Q: What are the different methods for producing inconel powder?
A: Common production methods include gas atomization, water atomization, vacuum induction melting followed by gas atomization, and rotating electrode process. Each method produces powder with different characteristics.
Q: How is inconel powder used in metal injection molding?
A: Inconel and cobalt-based powders are used to manufacture complex net-shaped components with small features using powder injection molding followed by debinding and sintering steps.
Q: What is the typical price range for Inconel 718 powder for additive manufacturing?
A: For additive manufacturing, spherical Inconel 718 powder of 15-45 micron size range costs between $100 to $220 per kg based on quantity and quality requirements.
Q: What are some alternatives to inconel alloys in high temperature applications?
A: Some alternatives include stainless steels like 310 and 330, cobalt-based alloys, titanium alloys, and iron-nickel alloys. However, inconel remains superior in terms of temperature capability.
Q: What are some of the latest developments in inconel powder alloys?
A: New inconel powder alloys include IN792, IN597, IN617, and IN713 with improved high temperature strength, low density, oxidation and creep resistance for demanding applications.
Q: What is the benefit of using inconel powder for additive manufacturing?
A: Inconel powder enables printing complex and lighter components with superior high temperature properties compared to cast alloys for aerospace and rocket nozzle applications.
Conclusion
Inconel nickel-based superalloy powders offer exceptional performance at high temperatures, corrosion resistance across various media, and useful non-magnetic properties. This guide summarizes the composition, manufacturing methods, specifications, pricing, advantages, and applications of different inconel powder varieties to support engineers and technical teams in procuring and utilizing this advanced material. With continued development of newer alloys and lower cost powder production methods, inconel powders will find increased applications in critical systems like aerospace engines, nuclear reactors, and chemical plants.


