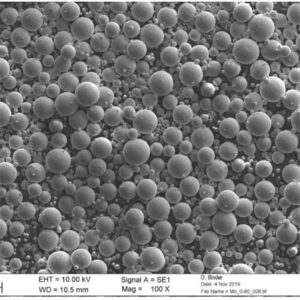
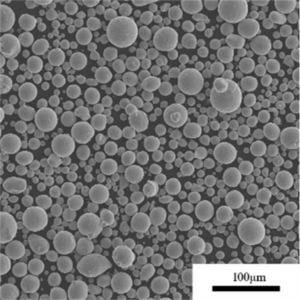
Overview of gas atomized metal powder
Gas atomized metal powder refers to metallic particulate materials produced by atomizing molten alloy feedstock with high velocity inert gas jets. This imparts a spherical morphology ideal for additive manufacturing, metal injection molding, and other applications.
Gas atomization features:
- Excellent control over particle shape, size distribution
- Applicable to reactive alloys including titanium, aluminum
- Provides high purity starting material for advanced processes
- Powders tailored for hot isostatic pressing, heat treatment
- Supports precise repeatable powder characteristics
Continue reading to learn about composition options, particle qualities, usage applications, and specifications for gas atomized powders.

Alloy Types of gas atomized metal powder
Various alloys are gas atomizeable into fine spherical powders:
| Alloy Category | Materials | Compositions |
|---|---|---|
| Stainless steels | 304, 316, 17-4PH, 303, 410 | Fe/Cr/Ni + trace elements |
| Tool steels | H13, M2, M4 | Fe + V, Mo, W carbides |
| Cobalt alloys | CoCr, CoCrW, CoCrMo | Co/Cr + tungsten/molybdenum |
| Nickel alloys | Inconel 625 & 718 | Ni/Cr/Fe/Mo |
| Titanium alloys | Ti-6Al-4V, Ti-6242 | Ti/Al/V/Sn/Zr/Mo |
Table 1: Overview of alloy systems commercially available in gas atomized powder
Specialty additive manufacturing and industry-specific alloys for aerospace/biomedical use may have minimum order quantities or lead times.
Powder Characteristics
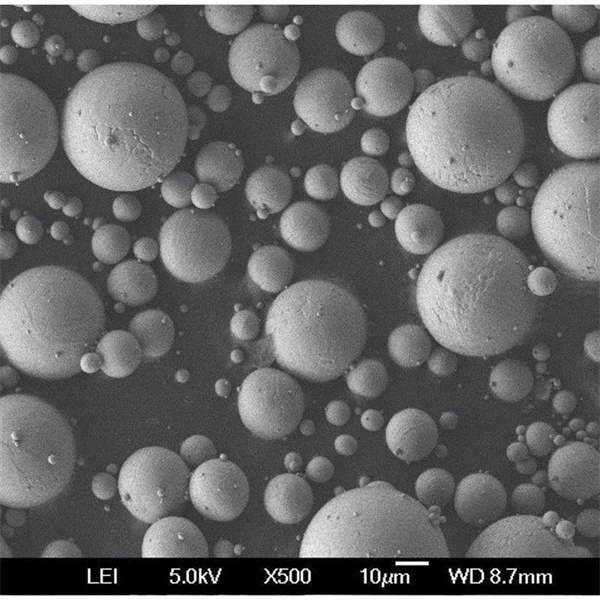
Typical particle characteristics achieved via inert gas atomization:
| Characteristic | Details | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Particle shape | Highly spherical | Improves powder flow and packing density |
| Size range | 10 μm to 150 μm | Controlled distribution optimized for end use |
| Composition | Alloying maintained within ± 0.5 wt% | Preserves mechanical properties |
| Purity | Up to 99.9% achievable | Reduces contaminants and inclusions |
| Surface Oxides | <50 nm thick passivation layer | Maintains excellent powder recyclability |
Table 2: Overview of particle qualities in gas atomized metal powders
Precise properties repeatably produced to meet certification needs across aerospace, medical, automotive and industrial categories.
Manufacturing Process
- Typical steps in inert gas atomization:
- Induction or arc melting forms alloy melt under protective cover gas
- High purity inert gas (Ar or N2) forced through specialized nozzles
- Molten stream breaks into fine droplets rapidly cooling into powders
- Powders settle into collection hoppers below
- Classified via sieves to normalize distribution
- Packaged and shipped to clients in protective atmosphere
- Critical process parameters:
- Nozzle design – governs particle size distribution
- Gas pressure – affects particle velocity and cooling rate
- Melt pouring rate – influences size distribution shape
- Environment (vacuum vs. controlled atmosphere) depends on reactivity
Applications of gas atomized metal powder
| Application | Benefits | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Additive manufacturing | High density parts from excellent powder flow and packing | Aerospace components, medical implants |
| Metal Injection Molding | Good moldability for small intricate shapes | Turbine blades, nozzle components |
| Thermal spray coatings | Dense coatings from deformable particle impacts | Wear-resistant surfaces |
| Braze pastes | Join complex geometries | Heat exchangers, electrical contacts |
| Hot Isostatic Pressing | Minimize closure issues with spherical particles | Consolidate cast turbine blades |
| Heat treatment precursors | Tailorable grain structure | Precipitation hardening alloys |
Table 3: Overview of applications leveraging qualities of gas atomized metal powders
The consistency and purity offered by gas atomization suits most advanced metal powder processes where repeatability is critical.
Specifications of gas atomized metal powder
Gas atomized powders are validated against various standard specifications:
| Standard | Description |
|---|---|
| ASTM B214 | Validation using optical microscopy for uniformity and lack of satellites |
| AMS 7008 | Aerospace material specification including inert gas atomization method |
| ASTM F3049 | Standard guide for characterizing properties of metal powders for AM |
| ASTM F3056 | Specification for additive manufacturing nickel alloy powders |
| ISO 21818 | Specification for DMLS/SLM production grade stainless steels |
Table 4: Industry standards commonly applied to inert gas atomized powders
Reputable producers will provide full certification paperwork and testing results for each powder lot to validate compliance.
Suppliers and Pricing
| Supplier | Materials | Indicative Pricing |
|---|---|---|
| Sandvik Osprey | Ti alloys, Ni alloys, tool steels | $100+ per kg |
| Carpenter Additive | Stainless steels, cobalt alloys, Cu | $50 – $150 per kg |
| Praxair | Ti alloys, Al alloys, silicon powders | $100+ per kg |
| LPW Technology | Tool steels, stainless steels, Inconels | $50 – $500 per kg |
| SLM Solutions | Custom alloy development | $250+ per kg |
Table 5: Selection of companies supplying gas atomized metal powders with approximate pricing
Most suppliers offer standard alloys with 2-4 week lead times in small quantities. Custom formulations and unique particle optimization is also possible working directly with gas atomization vendors.
Pros and Cons vs Alternatives
| Parameter | Gas Atomization | Water Atomization | Plasma Atomization |
|---|---|---|---|
| Particle morphology | Highly spherical | More irregular spheroids | Mostly spherical |
| Particle size distribution | Tight distribution, tailorable | Wider distribution | Tight distribution |
| Alloys compatible | Most commercial alloys | Limited alloys | Wide range including reactive metals |
| Cost per kg | Moderate $50-150 per kg | Lower $20-100 per kg | Higher $150-500 per kg |
| Productivity rates | Up to 10,000 kg per day capacity | Very high >50,000 kg per day | <1,000 kg per day |
Table 6: Comparison of gas atomization against alternative powder production methods
Gas atomization strikes an optimal balance between capabilities and economics while delivering powder volumes suited for commercial production.
Limitations
- Minimum batch sizes dictate use of 100kg+ material to justify machine setup
- Limited ability to economically atomize high melting point alloys like tungsten
- Powders not as spherical as plasma atomization and contain some satellites
- Oxide thickness slightly higher than vacuum plasma alternatives
- Steep initial capital costs around $1-5 million for turnkey system
- Requires improved powder handling/storage compared to virgin materials

FAQ
Q: What is the benefit of gas atomized powder over virgin materials for part production?
A: Gas atomized powders offer superior consistency and repeatability. Engineering the powder morphology and grain structure from the start enables mature processes producing certified components meeting the highest industry requirements in aerospace and medical sectors.
Q: What precautions are necessary when handling gas atomized powders?
A: As fine metallic materials prone to oxidation, inert storage and handling protocols are recommended. These include moisture-controlled argon filled glove boxes and workers wearing personal protective equipment to minimize explosion, inhalation or contamination risks. Never allow contact with water or organic compounds. Special facility construction is not necessarily required though local regulations may apply.
Q: What level of repeatability can be expected lot-to-lot with gas atomized powders?
A: Reputable producers guarantee powder distributions within ±10% between batches. Minor variations still warrant re-optimization as standard practice even from the same powder supplier if acceptable component tolerances are tight. Certificates of analysis document consistency.
Q: How long can unused gas atomized powders remain viable in storage?
A: Best practice stores powder in protective argon in sealed containers avoiding temperature extremes. If kept below 30°C and 50% relative humidity with minimal oxygen and moisture, powders lasts many months before needing refresh cycles in the glove box to maintain flow and reuse properties.
Q: What technical support do powder vendors provide for part qualification and certification?
A: Reputable vendors have material scientists and validation personnel to give application guidance and interface with part buyers through the testing process to certificate powders. They want demonstrated repeatability meeting regulated standards to expand use of materials in more demanding applications. Expect detailed paperwork and protocols from any established supplier.