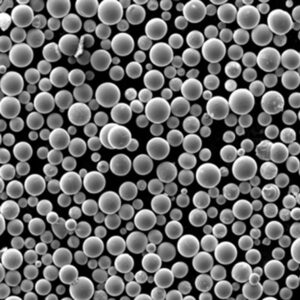
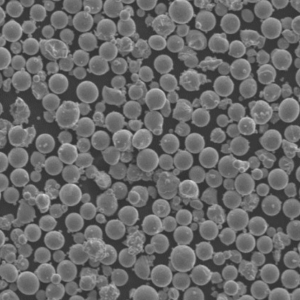
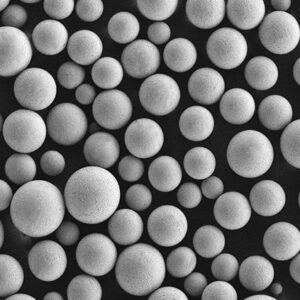
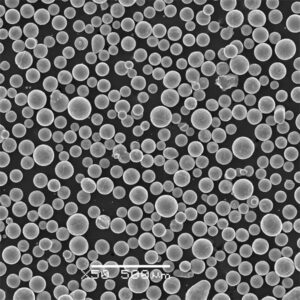
Aluminium alloy powder refers to powder metallurgy forms of aluminium alloys. Aluminium powders find use in various applications due to their lightweight, high strength, corrosion resistance, thermal conductivity, and electrical conductivity.
Overview of Aluminium Alloy Powder
Aluminium alloy powder is produced by atomization of molten alloys into fine droplets which solidify into powder particles. The composition and properties of the alloy powder can be tailored based on requirements.
Key details about aluminium alloy powder:
- Produced by atomization of aluminium alloys into fine powder
- Particle size ranges from few microns to millimeters
- Spherical, irregular, or flake particle shapes
- Variety of alloying elements used – Si, Mg, Zn, Cu etc.
- Properties dependent on alloy composition
- Lightweight, high strength, corrosion resistance
- Used for additive manufacturing, thermal spray, MIM etc.
Aluminium Alloy Powder Types
| Type | Composition | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Pure Al | 99%+ Al | Low strength, high electrical conductivity |
| 1000 series | Al + Mn, Fe, Si | Work-hardenable, higher strength |
| 2000 series | Al-Cu | Heat treatable, high strength |
| 5000 series | Al-Mg | Moderate to high strength |
| 6000 series | Al-Mg-Si | Medium to high strength |
| 7000 series | Al-Zn | Highest strength |

Aluminium Alloy Powder Composition
Aluminium alloy powders contain aluminium as the base metal along with alloying elements. Some common alloy additions include:
- Silicon – improves castability and welding characteristics
- Magnesium – increases strength through precipitation hardening
- Copper – highest strengthening effect, but reduces corrosion resistance
- Zinc – enhances strength through precipitation hardening
- Manganese – increases strength without reducing ductility
- Chromium – improves high temperature strength
- Zirconium – grain structure refiner giving uniform properties
Exact composition is specified by 4 digit numerical designations defined in various international standards.
Aluminium Alloy Powder Properties
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Strength | Varies from low to very high strength depending on alloy type and condition |
| Density | Around 2.7 g/cm3, making it much lighter than steels |
| Electrical conductivity | High but less than pure aluminium, varies by alloy |
| Thermal conductivity | High but alloying additions reduce it from pure Al value |
| Corrosion resistance | Generally good due to protective oxide layer but varies by alloy composition |
| Weldability | Typically good but some alloys can lose strength |
| Workability | Softer low alloy powders allow extensive forming |
| Cost | Higher than steel powder but more economical than titanium |
Aluminium Alloy Powder Characteristics
| Parameter | Details |
|---|---|
| Particle shape | Spherical, irregular, flakes |
| Particle size | From 1 micron to 1000 micron |
| Size distribution | Varies from tight distributions to wide ranges |
| Apparent density | Around 2.5 g/cm3 |
| Tap density | Around 2.7 g/cm3 |
| Flow rate | Important for powder handling and processing |
| Compressibility | Determines final part density achieved |
Aluminium Alloy Powder Applications
Aluminium alloy powders find usage across various industries due to their beneficial properties:
| Application | Details |
|---|---|
| Additive manufacturing | Used in powder bed fusion and directed energy deposition |
| Metal injection molding (MIM) | Low cost high volume production of complex parts |
| Thermal spray coatings | Provide wear and corrosion protection for components |
| Powder forging | Produces net shape blanks for downstream processing |
| Welding | Added to provide alloying elements for weld filler metal |
| Pyrotechnics | Fine reactive powders used to produce effects or gas |
| Brazing | Used as filler material to join aluminium components |
Additive Manufacturing Using Aluminium Alloy Powder
Additive manufacturing techniques like selective laser melting (SLM), direct metal laser sintering (DMLS) and electron beam melting (EBM) use aluminium alloy powder feedstock to produce end-use components across aerospace, automotive and industrial sectors.
Some benefits of AM with Al alloy powder:
- Complex geometries not possible by conventional methods
- Reduced weight through optimized designs
- Part consolidation improves manufacturing efficiency
- Properties comparable to wrought products in most alloys
- Minimal material wastage compared to subtractive techniques
Current limitations in AM using Al powder include:
- High reflectivity demands higher power lasers
- High thermal conductivity makes heat control difficult
- Cost is higher compared to conventional techniques for production volumes
- Porosity control and anisotropic properties remain a challenge
- Surface finish quality currently inferior to machined parts
- Restricted alloy choice compared to wrought alloys
Ongoing process developments continue to improve quality, capabilities and economics of additively manufactured aluminium components.
Metal Injection Molding with Aluminium Alloy Powder
Metal injection molding (MIM) can produce complex, tight tolerance, net-shape metallic components using aluminium alloy powder feedstock at relatively low costs.
Benefits of MIM with aluminium alloy powder:
- Intricate parts with walls and features < 0.5 mm
- Tight dimensional tolerances approaching +/- 0.1%
- As-sintered properties similar to PM or cast alloys
- Near full density and good surface finish
- Automated high volume production possible
Limitations for MIM using aluminium powders:
- More difficult to process than steel and harder tooling needed
- Higher melting point increases molding machine demands
- Reactivity limits binder choices for feedstock formulation
- Secondary finishing may be needed to achieve final properties
Despite challenges, MIM continues to expand into high performance sectors due to advantages over other manufacturing approaches for complex aluminium alloy components.
Aluminium Alloy Powder for Thermal Spray
Aluminium alloy powders like AA2024, AA5083 and AA7075 are commonly used as feedstock material for various thermal spray coating processes to protect components against wear, corrosion, heat etc.
| Process | Description |
|---|---|
| Combustion Wire-arc | Two wire arc metalizing process with simple equipment |
| Flame spraying | Powder injected into oxygen-fuel gas flame |
| High Velocity Oxy-Fuel (HVOF) | High kinetic energy spray minimizing porosity |
| Cold spraying | Solid state deposition via high speed powder impact |
| Plasma spraying | Most versatile technique with hot ionized gas |
Benefits of using Al alloy powder for thermal spray coatings:
- Provides wear and corrosion protection
- Restores oversized parts to original dimensions
- Minimal heat input prevents substrate warpage
- As-sprayed coatings or with infiltration for full density
- Lower material costs than high alloy weld overlays
- Simpler processing than many wrought alloys
Aluminium Alloy Powder Specifications
Aluminium alloy powders are produced according to various standard specifications that define the acceptable composition limits, particle size ranges, shape control etc.
| Standard | Description |
|---|---|
| AMS 4200 | Aerospace material specification for atomized Al alloy powder |
| ASTM B602 | Standard specification for Al alloy powders |
| EN 1706 | European standard specification for atomized Al powders |
| ISO 13318 | International standard for gas and water atomized Al powders |
| DIN 50125 | German national standard for atomized Al powders |
Specifications allow customers to procure powder suitable for their specific application and process requirements.
Sizes of Aluminium Alloy Powder
Various size ranges of aluminium alloy powder are produced depending on end use:
- Ultrafine powder < 10 microns for reactive applications
- Fine powder 15 – 45 microns commonly for thermal spray
- Medium powder 45 – 100 microns widely used size
- Coarse powder up to 150 microns for specialty applications
Larger particles over 180 microns mainly used in cold spray processes for thicker coatings. Control of particle size distribution is also important for some applications.
Grades of Aluminium Alloy Powder
Aluminium alloy powder is manufactured into different established grades based on the alloy type:
- 1xxx series powders – AA1100, AA1350
- 2xxx series powders – AA2014, AA2024, AA2219, AA2519
- 5xxx series powders – AA5083, AA5654
- 6xxx series powders – AA6061, AA6082
- 7xxx series powders – AA7050, AA7075
Higher number series indicate higher alloying levels and strength. Custom alloy compositions are also possible for proprietary grades.
Aluminium Alloy Powder Comparison
| Parameter | Cold Gas Atomization | Water Atomization |
|---|---|---|
| Particle shape | Highly spherical | More irregular, satellites |
| Particle size range | 15 – 180 microns | 5 – 350 microns |
| Size distribution | Tighter control | Wider distribution |
| Apparent density | Higher | Lower |
| Production rate | Lower | Higher |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
Water atomized powders tend to have a cost advantage but suffer from less sphericity and broader particle distributions compared to gas atomized aluminium alloy powder.
Aluminium Alloy Powder Standards
Key standards for aluminium alloy powder:
| Standard | Organization | Description |
|---|---|---|
| AMS4200 | SAE | Aerospace material specification |
| ASTM B602 | ASTM | Chemical compositions and sieve sizes |
| EN1706 | CEN | European standard specification |
| ISO13318 | ISO | International standard for gas atomized and water atomized forms |
Various national and organizational standards help ensure quality and consistency of aluminium alloy powder supply.
Global Suppliers of Aluminium Alloy Powder
| Supplier | Location | Capabilities |
|---|---|---|
| Valimet Inc. | USA | Wide range of atomization, large capacity |
| Sandvik Osprey | UK | Leading supplier of controlled powders |
| TLS Technik GmbH | Germany | Specialist in gas and water atomized powders |
| Fukuda Metal Foil & Powder Co. | Japan | Broad alloy offerings |
| SCM Metal Products | Singapore | Focus on aluminum and copper alloys |
Pricing for Aluminium Alloy Powders
Price for aluminum alloy powder varies based on:
- Alloy grade and characteristics
- Particle shape and size specifications
- Purchase quantity and lot size
- Regional tariffs and transportation
| Type | Price Range |
|---|---|
| 1xxx series | $5 – $15 per kg |
| 2xxx series | $10 – $30 per kg |
| 5xxx series | $15 – $35 per kg |
| 6xxx series | $20 – $40 per kg |
| 7xxx series | $30 – $60 per kg |
Prices above are approximate ranges for reference purpose only. Contact suppliers for exact current pricing based on your specific needs.
Advantages and Limitations of Aluminium Alloy Powder
Advantages
- Lightweight compared to steel and titanium alloys
- Achieve strengths exceeding many wrought product forms
- Composition and properties can be customized
- Low raw material cost compared to titanium or nickel alloys
- Good corrosion resistance in many environments
- High thermal and electrical conductivity
- Variety of production processes possible from powder
Limitations
- Lower strength than high alloy steels at elevated temperatures
- Reactivity limits some processing approaches and applications
- Producing high integrity large cross sections remains challenging
- Cost is higher than conventional carbon steel powders
- Some fatigue sensitive applications may require wrought products
- Anisotropic properties and porosity issues in AM components

Frequently Asked Questions
What are the most common alloys used as aluminium alloy powder?
The most common alloy powders are: 2xxx series such as 2014 and 2024, 5xxx alloys like 5083, 6xxx alloys including 6061 and 6082, and 7xxx alloys with 7050 and 7075 being popular.
What particle size is best for metal injection molding using aluminium powders?
A particle size range between 15-45 microns is typically recommended for metal injection molding using aluminium alloy powders.
What types of atomization processes can produce aluminium alloy powder?
Gas atomization and water atomization are the two main industrial processes used. Rotating disk atomization method can also produce aluminum powders.
What is the benefit of using 5xxx series aluminum alloys for thermal spraying?
5xxx series Al alloys like 5083 have excellent corrosion resistance while remaining dimensionally stable at elevated temperatures making them suitable for thermal spray coatings for marine and chemical exposures.
What affects the pricing of aluminum alloy powder?
The alloy composition, particle characteristics like size and shape, order volume, regional tariffs and transportation costs determine the final pricing from different aluminum powder suppliers.
What standards apply to aluminum alloy powders for additive manufacturing uses?
Key standards include ASTM B602, AMS4200, EN1706, and ISO 13318. Additional AM-specific standards are under development to address process-related requirements.
Can aluminum alloy powder be reused?
Reusing aluminum powder is generally not recommended for critical applications. Storage conditions can allow moisture pickup and oxidation limiting powder performance. Minor reuse may be possible in non-critical applications with appropriate testing.
Are higher number aluminum alloys always stronger than lower number alloys?
In general, higher number 2xxx, 6xxx, and 7xxx series powders have higher strength than 1xxx or 5xxx alloys, but significant overlap can exist based on exact composition, powder characteristics and processing history. Always check supplier data for guaranteed powder properties.
Why is porosity and anisotropy a concern for AM made aluminum components?
High thermal conductivity and reflectivity of aluminum combined with rapid solidification during laser or e-beam melting hinders optimal fusion and gas bubble escape leading to defects. Different mechanical properties parallel and transverse to build layers also arise.
Can I mix different aluminum alloy powders to create custom grades?
It is generally not advisable to mix powders to create intermediate or custom alloys due to risks of incomplete mixing, alloy reactions, or inadequate particle bonding during part manufacture. Consult closely with your powder supplier when exploration property combinations.