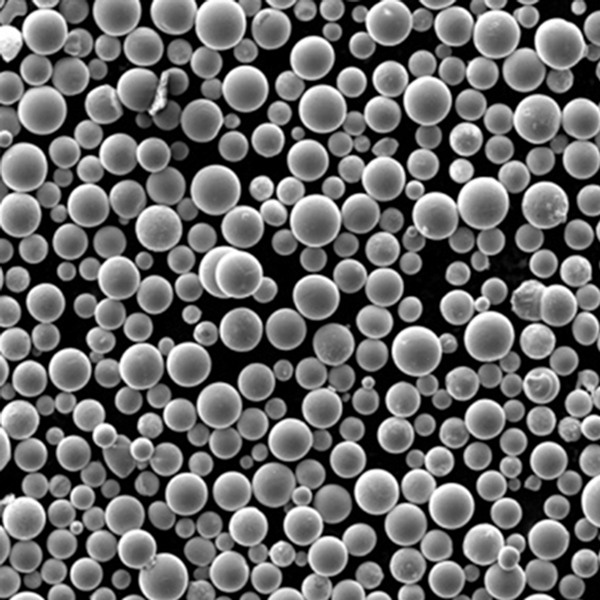
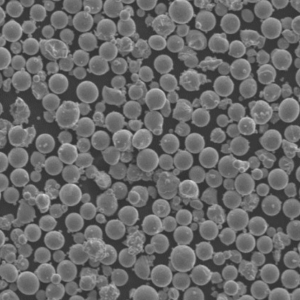
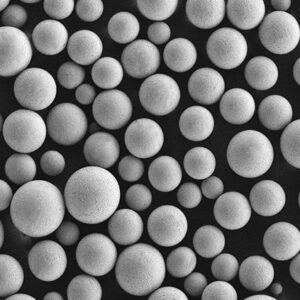
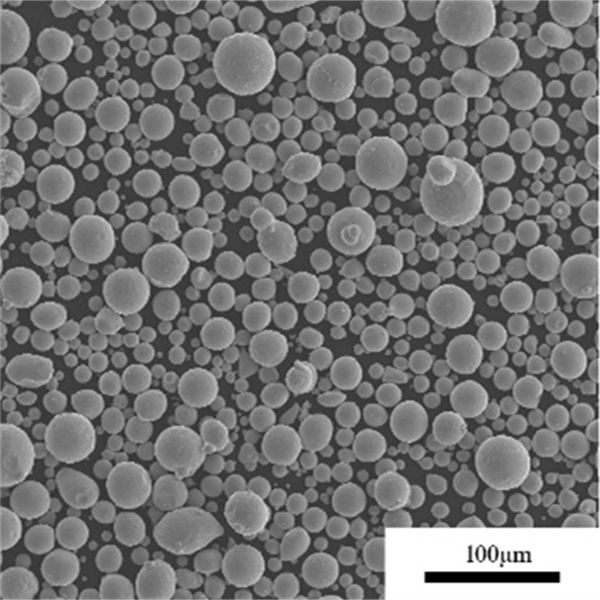
Pure Copper Powder
Pure copper powder contains 99.5% or higher copper content. It provides excellent thermal and electrical conductivity combined with good corrosion resistance, solderability, and bio-compatibility.
Low MOQ
Provide low minimum order quantity to meet different needs.
OEM & ODM
Provide customized products and design services to meet unique customer needs.
Adequate Stock
Ensure fast order processing and provide reliable and efficient service.
Customer Satisfaction
Provide high quality products with customer satisfaction at the core.
share this product
Table of Contents
Overview of Pure Copper Powder
Pure copper powder contains 99.5% or higher copper content. It provides excellent thermal and electrical conductivity combined with good corrosion resistance, solderability, and bio-compatibility.
Key properties and advantages of pure copper powder:
Pure Copper Powder Properties and Characteristics
| Properties | Details |
|---|---|
| Composition | 99.5% or higher copper content |
| Density | 8.94 g/cc |
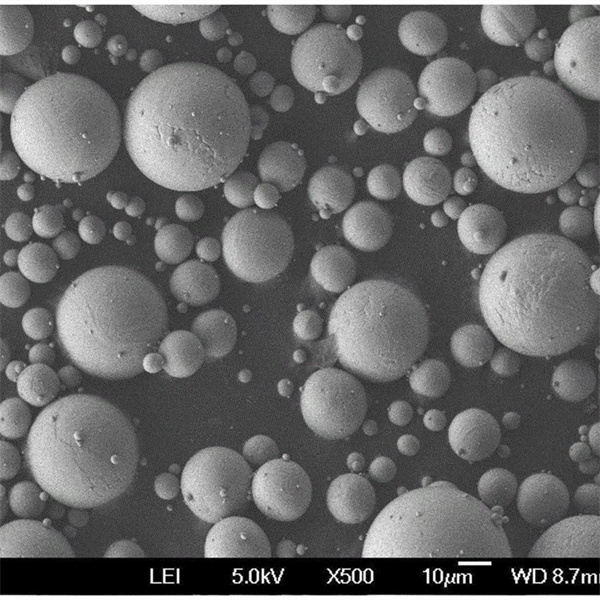
| Particle shape | Spherical, irregular |
| Size range | 1-150 microns |
| Apparent density | Up to 50% of true density |
| Conductivity | Excellent, second only to silver |
| Solderability | Excellent due to oxidation resistance |
| Bio-compatibility | High, safe for food contact |
Pure copper powder is ideal for applications like welding products, brazing alloys, friction materials, diamond tools, electrical contacts, and metal injection molding.
Pure Copper Powder Composition
Typical composition of pure copper powder:
Pure Copper Powder Composition
| Element | Weight % |
|---|---|
| Copper (Cu) | 99.5% min |
| Oxygen (O) | 0.05% max |
| Lead (Pb) | 0.005% max |
| Other impurities | 0.005% max |
- Copper provides excellent conductivity and corrosion resistance
- Oxygen present as impurity affects conductivity and sintering
- Lead and other impurities carefully controlled
High copper content, low oxide, and minimal impurities result in excellent electrical and thermal conductivity combined with good mechanical properties.
Pure Copper Powder Physical Properties
Pure Copper Powder Physical Properties
| Property | Values |
|---|---|
| Density | 8.94 g/cc |
| Melting point | 1083°C |
| Thermal conductivity | 400 W/mK |
| Electrical resistivity | 1.72 μΩ-cm |
| Recrystallization temperature | 200-300°C |
| Curie temperature | -269°C |
- High density compared to magnesium or aluminum
- Excellent thermal conductivity for heat dissipation
- Low electrical resistivity provides high conductivity
- Recrystallization enables sintering and improves ductility
- Resistivity increases above Curie point
These properties make pure copper suitable for highly conductive components like electrical contacts and brushes.
Pure Copper Powder Mechanical Properties
Pure Copper Powder Mechanical Properties
| Property | Values |
|---|---|
| Tensile strength | 220-340 MPa |
| Yield strength | 69-172 MPa |
| Elongation | 35-60% |
| Hardness | 45-90 HB |
| Modulus of elasticity | 110-130 GPa |
| Compressive strength | 500-700 MPa |
- Good combination of strength and very high ductility
- Relatively low hardness and high malleability
- Moderate strength compared to high strength alloys
- Properties depend on factors like porosity and grain size
The properties make pure copper suitable for soft, highly conductive components requiring good deformation and compressive strength.
Pure Copper Powder Applications
Typical applications of pure copper powder include:
Pure Copper Powder Applications
| Industry | Uses |
|---|---|
| Electricals | Contacts, brushes, welding electrodes |
| Electronics | Conductive adhesives, RF shielding |
| Automotive | Brushes, bushings, bearings |
| Industrial | Diamond tools, casting molds |
| Manufacturing | Brazing alloys, powder metallurgy |
| Friction products | Brake pads, clutch discs |
Some specific product uses:
- Sliding electrical contacts and brushes
- Heat sinks and thermal management components
- Welding rods, brazing pastes, and solder filler metal
- Metal matrix composites like diamond tools
- Net shape components made via metal injection molding
- Pump bushings, impellers, and other wear parts
The high conductivity, corrosion resistance, bio-compatibility and moderate strength make pure copper suitable for this diverse range of electrical, thermal, and moderate wear applications across all industries.
Pure Copper Powder Specifications
Key specifications for pure copper powder include:
Pure Copper Powder Specifications
| Standard | Description |
|---|---|
| ASTM B602 | Specification for high purity electrolytic copper powder |
| JIS H2111 | Specs for electrolytic copper and copper alloy powders |
| ISO 3497 | Specification for general purpose copper powders |
| ASTM B243 | Guidance on apparent density and flow rate |
These define:
- Minimum 99.5% copper content
- Limits on impurities like oxygen and lead
- Required powder characteristics
- Apparent density and flow rate
- Approved production method – electrolytic
- Sampling and testing protocols
Meeting these specifications ensures suitability for applications needing high thermal and electrical conductivity combined with good mechanical properties.
Pure Copper Powder Particle Sizes
Pure Copper Powder Particle Size Distribution
| Size | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| 1-10 microns | Ultrafine grade used in microelectronics |
| 10-30 microns | Fine grade suitable for sintering |
| 30-150 microns | Coarse grade has good flow for pressing |
- Finer sizes provide higher sintered density
- Coarser powder has improved flowability
- Size range tailored based on targeted application
- Both spherical and irregular shapes available
Controlling particle size distribution optimizes pressing behavior, sintered density and final part properties.
Pure Copper Powder Apparent Density
Pure Copper Powder Apparent Density
| Apparent Density | Details |
|---|---|
| Up to 50% of true density | For irregular powder morphology |
| 3.5-5.0 g/cc typical | Improves with greater packing density |
- Higher apparent density improves powder flow and compressibility
- Irregular morphology limits maximum packing density
- Values up to 60% achievable with spherical powder
- High apparent density enables easier compaction
Higher apparent density leads to more efficient powder pressing and sintering to full density.
Pure Copper Powder Production
Pure Copper Powder Production
| Method | Details |
|---|---|
| Electrolysis | Copper cathodes dissolved anodically into Cu+ ions and deposited on stainless steel cathodes |
| Ball milling | Coarse powder broken down and classified into specific sizes |
| Annealing | Softens the powder particles and improves compressibility |
| Reducing atmosphere | Prevents oxidation of particles during production |
- Automated electrolytic process allows large scale production
- Milling and sieving provides controlled particle size distribution
- Annealing facilitates pressing and handling
- Strict process control ensures high purity and repeatable quality
Pure Copper Powder Pricing
Pure Copper Powder Pricing
| Factor | Impact on Price |
|---|---|
| Purity grade | Higher purity increases cost |
| Particle size | Ultrafine powder more expensive |
| Order quantity | Bulk orders have lower per unit pricing |
| Production method | Additional processing increases cost |
| Packaging | Special packaging like vacuum sealing adds cost |
Indicative Pricing
- Ultrafine pure copper powder: $15-25 per kg
- Coarse pure copper powder: $10-15 per kg
- Large volume pricing can be 40% lower
Pricing depends on purity, particle size, production method, order quantity, packaging etc.
Pure Copper Powder Suppliers
Pure Copper Powder Suppliers
| Company | Location |
|---|---|
| Kymera International | USA |
| GGP Metalpowder | Germany |
| American Chemet Corporation | USA |
| Shanghai CNPC Powder Material | China |
| Mitsui Kinzoku | Japan |
| Nuclead | France |
Selection factors for suppliers:
- Purity levels and grades offered
- Production capacity and lead times
- Average particle size ranges
- Customization of size distribution
- Packaging options and order quantities
- Pricing levels based on volume
- Compliance with international specifications
Pure Copper Powder Handling and Storage
Pure Copper Powder Handling
| Recommendation | Reason |
|---|---|
| Ensure proper ventilation | Prevent exposure to fine particles |
| Use appropriate PPE | Avoid accidental ingestion |
| Follow safe protocols | Reduce health hazards |
| Avoid ignition sources | Flammable dust hazard |
| Ground equipment | Prevent static discharge |
| Use non-sparking tools | Prevent possibility of ignition |
Storage Recommendations
- Store in stable containers in a cool, dry area
- Limit exposure to acids, ammonia, acetylene
- Maintain temperatures below 30°C
Proper precautions during handling and storage help preserve purity and prevent safety issues.
Pure Copper Powder Inspection and Testing
Pure Copper Powder Testing
| Test | Details |
|---|---|
| Chemical analysis | ICP or XRF verifies composition |
| Particle size distribution | Laser diffraction analysis |
| Apparent density | Hall flowmeter test per ASTM B212 |
| Powder morphology | SEM imaging of particle shape |
| Tap density test | Density measured after mechanical tapping |
| Flow rate analysis | Gravity flow through a specified funnel |
Testing ensures the powder meets the required purity levels, particle characteristics, density specifications, morphology and flowability as per applicable standards.
Pure Copper Powder Pros and Cons
Advantages of Pure Copper Powder
- Excellent thermal and electrical conductivity
- Good corrosion resistance and bio-compatibility
- High purity provides optimal performance
- Easy to sinter and compress into high density components
- Ductile and malleable
- Recyclable and environmentally sustainable
Limitations of Pure Copper Powder
- Lower strength than many alloy powders
- Moderate high temperature oxidation resistance
- Heavy compared to magnesium or aluminum
- Not suitable for high wear or load bearing applications
- Sensitive to contamination from zinc and sulfur
- Gradually tarnishes over time if uncoated
Comparison With Brass and Bronze Powders
Pure Copper vs. Brass and Bronze Powders
| Parameter | Pure Copper | Brass/Bronze |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 8.94 g/cc | 8.7-8.8 g/cc |
| Strength | 220-340 MPa | 350-550 MPa |
| Conductivity | Excellent | Good |
| Corrosion resistance | Excellent | Good |
| Cost | Low | Moderate |
| Uses | Electrical, thermal | Hardware, decorative |
- Pure copper has higher conductivity and ductility
- Brass/bronze offer higher strength
- Pure copper better suited for thermal management
- Brass/bronze used for hardware and decorative items
Pure Copper Powder FAQs
Q: What are the main applications of pure copper powder?
A: Main applications include electrical contacts and brushes, welding rods, brazing alloys, diamond tools, heat sinks, net shape components made via powder metallurgy, friction materials, and conductive adhesives.
Q: What precautions should be taken when working with pure copper powder?
A: Recommended precautions include proper ventilation, appropriate PPE, safe handling protocols, grounding equipment, avoiding ignition sources, using non-sparking tools, and storing in stable inert containers away from contaminants.
Q: How does pure copper powder differ from electrolytic tough pitch (ETP) copper?
A: Pure copper powder has 99.5% or higher copper content, while ETP copper powder has minimum 99.5% copper. Pure copper provides slightly higher conductivity but the two are mostly interchangeable for common applications.
Q: What affects the properties of parts made from pure copper powder?
A: Key factors are apparent density, powder composition, particle size distribution, compaction pressure, sintering parameters, presence of impurities, and final part porosity.
About Met3DP
Product Category
HOT SALE
CONTACT US
Any questions? Send us message now! We’ll serve your request with a whole team after receiving your message.