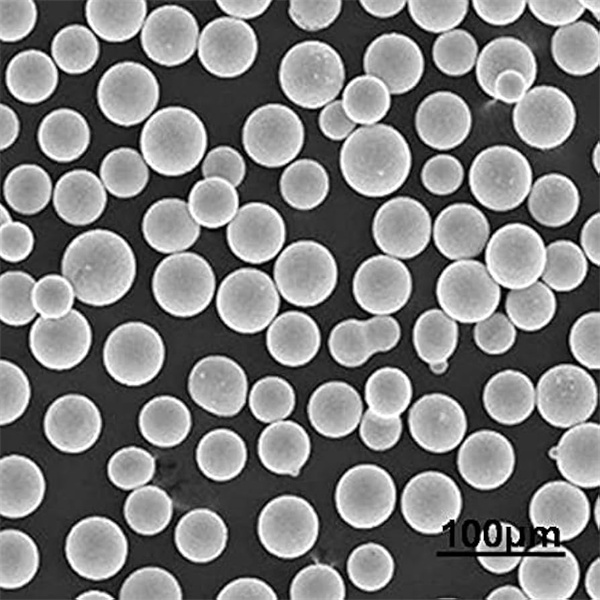
CPTi Powder
CPTi (chemically pure titanium) powder is a high purity titanium metal powder used in various applications requiring excellent corrosion resistance, high strength, low weight, and biocompatibility. It offers superior properties compared to other titanium grades and alloy powders.
Low MOQ
Provide low minimum order quantity to meet different needs.
OEM & ODM
Provide customized products and design services to meet unique customer needs.
Adequate Stock
Ensure fast order processing and provide reliable and efficient service.
Customer Satisfaction
Provide high quality products with customer satisfaction at the core.
share this product
Table of Contents
Overview of CPTi Powder
CPTi (chemically pure titanium) powder is a high purity titanium metal powder used in various applications requiring excellent corrosion resistance, high strength, low weight, and biocompatibility. It offers superior properties compared to other titanium grades and alloy powders.
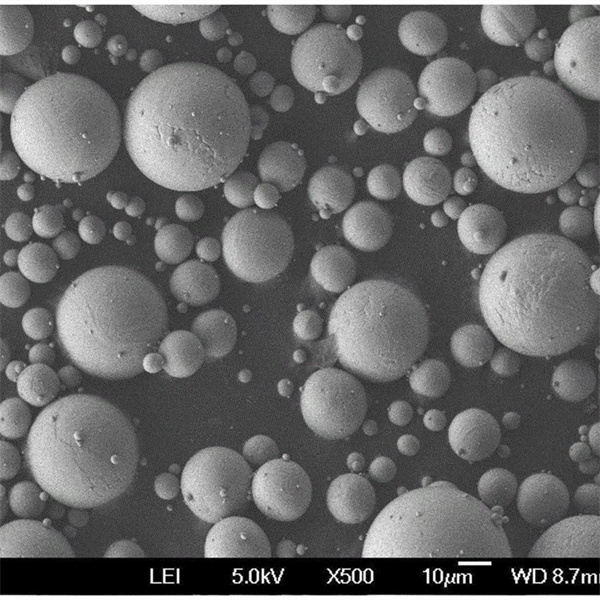
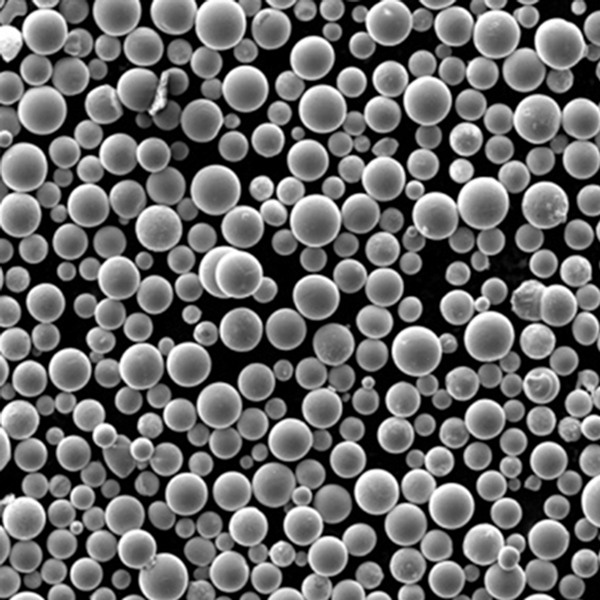
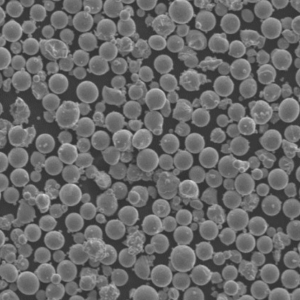
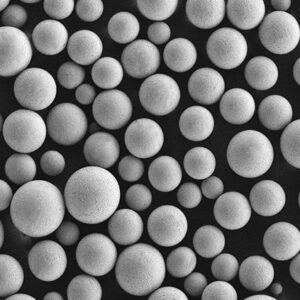
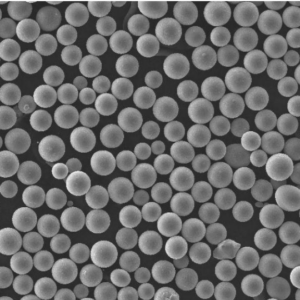
CPTi powder is produced by gas atomization process to achieve spherical powder morphology with minimal contamination. It has a particle size range of 15-150 microns generally. The high purity and cleanliness result in excellent flowability, packing density and sinterability.
Some key properties and advantages of CPTi powder include:
CPTi Powder Properties and Characteristics
| Properties | Details |
|---|---|
| Composition | 99.5% minimum Titanium. Low O, C, N, H, Fe impurities |
| Density | 4.5 g/cc |
| Flowability | Excellent due to spherical morphology |
| Sinterability | Excellent, achieves near full density |
| Particle shape | Predominantly spherical |
| Particle size range | 15-150 microns |
| Apparent density | 2.7-3.2 g/cc |
| Purity | Up to 99.995% Ti content |
| Impurities | Low oxygen, nitrogen, carbon, iron |
| Color | Dark gray with metallic luster |
CPTi Powder Key Advantages
- High purity improves performance and biocompatibility
- Spherical powder morphology provides good flow and packing
- Widely used for additive manufacturing, metal injection molding
- Corrosion resistance superior to stainless steel in many environments
- High strength-to-weight ratio
- Non-toxic and non-allergenic
- Can be alloyed to modify properties like strength
- Cost-effective compared to wrought titanium
CPTi powder is an excellent choice for parts and products requiring the optimum combination of strength, low weight, corrosion resistance, fatigue resistance, and biocompatibility.
It is used for diverse applications in aerospace, medical, automotive, chemical, and consumer industries.
CPTi Powder Composition and Purity Grades
CPTi powder composition has a minimum of 99.5% titanium content. The impurity levels of oxygen, nitrogen, carbon, hydrogen and iron are carefully controlled. Higher purity grades up to 99.995% Ti are also produced.
CPTi Powder Composition
| Element | Weight % |
|---|---|
| Titanium | 99.5% min |
| Oxygen | 0.08% – 0.40% |
| Carbon | 0.03% – 0.08% |
| Nitrogen | 0.01% – 0.05% |
| Hydrogen | 0.005% – 0.015% |
| Iron | 0.05% – 0.25% |
These impurity levels result in retainment of high strength and corrosion resistance associated with titanium metal. Specific alloying additions can also be made to modify properties like strength.
CPTi powder is available in different purity grades depending on requirements:
CPTi Purity Grades
| Grade | Purity | Particle Size | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| CPTi Grade 1 | 99.5% min | Medium, large | General use |
| CPTi Grade 2 | 99.9% | Fine, medium | Aerospace, medical |
| CPTi Grade 3 | 99.95% | Fine | Medical, dental |
| CPTi Grade 4 | 99.99% | Ultrafine | Implants, high purity uses |
Higher purity reduces risk of toxicity, improves biocompatibility for medical uses. It also improves performance in high temperature applications.
However, higher purity increases cost. So suitable grade is selected based on balanced trade-off for intended application.
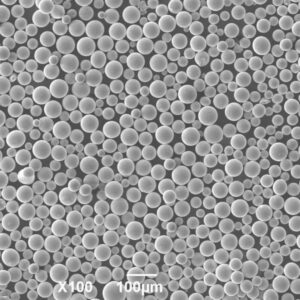
CPTi Powder Physical Properties
Key physical properties of CPTi powder which influence its processing and performance:
CPTi Powder Physical Properties
| Properties | Values |
|---|---|
| Density | 4.5 g/cc |
| Melting point | 1668°C |
| Thermal conductivity | 21.9 W/mK |
| Electrical resistivity | 53.8 ohm-cm |
| Young’s modulus | 107 GPa |
| Poisson’s ratio | 0.33 |
| Mohs hardness | 6 |
| Oxidation resistance | Up to 590°C in air |
- Density is quite low compared to other metals providing high strength-to-weight ratio
- Melting point is moderately high allowing use for elevated temperature applications
- Thermal conductivity is lower than other metals like aluminum or copper
- Electrical resistivity is relatively high making it suitable for corrosion resistant fasteners and connectors
- Hardness is similar to other titanium alloys but lower than high hardness metals
- Oxidation resistance improves with higher purity levels
These properties make CPTi suitable for lightweight structural parts needing high mechanical performance and corrosion resistance.
CPTi Powder Mechanical Properties
Mechanical properties represent the strength, hardness, and workability of the material. Important mechanical properties:
CPTi Powder Mechanical Properties
| Properties | Values |
|---|---|
| Tensile strength | 420 – 550 MPa |
| Yield strength | 380 – 470 MPa |
| Elongation | 15 – 30% |
| Hardness | 200-240 HV |
| Fatigue strength | 200-300 MPa |
- Tensile and yield strength are moderately high while elongation is reasonable
- Fatigue strength is excellent compared to other competing materials
- Hardness is similar or slightly lower than titanium alloys
- Properties depend on factors like purity, porosity, processing method
- Alloying with elements like Al, V, Mo can significantly increase the strength
The combination of good strength, ductility, fatigue life, and hardness provides balanced mechanical performance.
CPTi matches or exceeds the properties of stainless steels at a lower density. It offers the optimum trade-off between high strength and moderate ductility.
CPTi Powder Applications
CPTi powder is used across several industries owing to its excellent properties:
CPTi Powder Applications
| Industry | Application Examples |
|---|---|
| Aerospace | Engine components, airframe parts, fasteners |
| Medical | Implants, prosthetics, instruments |
| Automotive | Valves, connecting rods, springs |
| Chemical | Pumps, valves, tanks, pipes |
| 3D printing | Aerospace and medical components |
| Metal injection molding | Dental instruments, hardware |
| Investment casting | Turbine blades, golf club heads |
Some specific product applications include:
- Orthopedic and dental implants
- Surgical instruments and bio-implants
- Lightweight automotive engine parts like connecting rods
- Aerospace hydraulic tubing and components like bushings
- Food/chemical industry valves, pumps, pipes
- Watch cases, jewelry
- Sporting goods like golf clubs, bicycle frames
- Additive manufacturing of aerospace and medical parts
The non-toxic property allows use in products which come in contact with food, pharmaceuticals, and biological fluids.
Overall, CPTi powder provides the best balance of properties for lightweight structural parts across multiple industries.
CPTi Powder Specifications
Industrial specifications and standards are used to evaluate CPTi powder quality and to ensure performance consistency:
CPTi Powder Standards
| Standard | Description |
|---|---|
| ASTM B348 | Standard specification for titanium and titanium alloy powders |
| ASTM F67 | Standard specification for unalloyed titanium bars for surgical implants |
| ISO 5832-2 | Implant grade wrought titanium materials |
These standards specify requirements for:
- Chemical composition – percentages of titanium and impurity levels
- Physical properties like particle size distribution, flow rate, density
- Mechanical properties like tensile and yield strength
- Production method like argon gas atomization
- Quality assurance through sampling, testing and inspection
- Packaging and identification requirement
Reputable CPTi powder manufacturers produce material per ASTM standards and provide certification of compliance for critical applications.
CPTi Powder Particle Sizes
CPTi powder is produced in different particle size distributions based on application method:
CPTi Powder Particle Sizes
| Particle size | Typical size range | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Fine | 1-25 microns | Investment casting, MIM |
| Medium | 25-45 microns | Press and sinter, HIP |
| Coarse | 45-150 microns | Thermal and cold spraying |
- Fine powder provides high sintered density and surface finish
- Coarse powder has better flowability and is used for thermal spraying
- Medium size range offers a balance suitable for press-and-sinter
- Size distribution is optimized based on final part properties needed
- Spherical morphology is maintained across all size ranges
Controlling particle size distribution and morphology is critical to achieve high powder packing density and sintered part quality.
CPTi Powder Apparent Density
Apparent density or tap density indicates the packed density of powder:
CPTi Powder Apparent Density
| Apparent Density | Characteristics |
|---|---|
| 2.7 – 3.0 g/cc | Unalloyed CPTi powder |
| 3.0 – 3.2 g/cc | Alloyed CPTi powder |
| Up to 50% of true density | Due to voids between particles |
- Higher apparent density improves powder flow and compressibility
- Alloying elements like Al, V increase particle density
- Values up to 60% are possible with optimized powder
- High apparent density reduces press cycle time and improves part quality
Maximizing apparent density allows efficient powder pressing and sintering to full density. It improves manufacturing productivity.
CPTi Powder Production Methods
CPTi powder is commercially produced via gas atomization process using high purity Ti bars/rods:
CPTi Powder Production
| Method | Details |
|---|---|
| Gas atomization | High pressure argon gas disintegrates molten Ti stream into fine droplets, which solidify into spherical powder |
| Vacuum arc melting | High purity Ti input stock is refined to reduce gaseous impurities like O, N, H |
| Multiple melting | Ensures chemical homogeneity of raw material |
| Sieving | Classifies powder into different particle size distributions |
| Blending | Powders with different particle sizes are mixed in optimized ratios |
- Gas atomization enables large scale production of spherical CPTi powder
- Multiple steps produce high purity powder with controlled size and morphology
- Argon gas prevents contamination during atomization
- Post-processing provides customized powder grades for clients
Highly automated equipment allows efficient CPTi powder production with tight control over all attributes like purity, particle size distribution, morphology, and apparent density.
CPTi Powder Pricing
CPTi powder pricing depends on various factors:
CPTi Powder Pricing
| Factor | Impact |
|---|---|
| Purity | Price increases for higher purity |
| Particle size | Ultrafine powder is more expensive |
| Quantity | Price reduces for bulk order quantities |
| Production method | Multiple remelts increase cost |
| Packaging | Argon filled cylinders cost more |
| Testing/certification | Additional cost for more rigorous testing |
| Lead time | Faster delivery increases price |
Indicative pricing for medium particle size powder:
- CPTi Grade 1: $50-$100 per kg
- CPTi Grade 2: $100-$150 per kg
- CPTi Grade 3: $150-$300 per kg
- CPTi Grade 4: $300+ per kg
Reduced prices are typical for bulk orders exceeding several hundred kgs.
CPTi Powder Suppliers
Popular suppliers of CPTi Powder include:
CPTi Powder Suppliers
| Company | Location |
|---|---|
| Advanced Powders & Coatings | USA |
| Atlantic Equipment Engineers | USA |
| Reading Alloys, Inc. | USA |
| TLS Technik GmbH & Co. | Germany |
| AP&C | Canada |
| Xi’an Saite Metal Materials | China |
Factors to consider when selecting supplier:
- powder grade options
- average particle size ranges
- production capacity
- powder morphology and consistency
- packaging options
- lead time and delivery
- pricing
- compliance with ASTM standards
- inspection and testing processes
- quality assurance and control
CPTi Powder Handling and Safety
Safe powder handling practices should be followed:
CPTi Powder Handling
| Recommendation | Reason |
|---|---|
| Avoid inhalation | Due to small particle size |
| Use protective masks | Prevent ingestion through nose/mouth |
| Conduct handling in ventilated areas | Reduce airborne powder circulation |
| Use hazmat suits in large operations | Minimize skin contact |
| Ensure no ignition sources nearby | Powder can combust in oxygen atmosphere |
| Follow anti-static protocols | Prevent accidental fire due to buildup of static charge |
| Use non-sparking tools | Avoids possibility of ignition during handling |
| Store sealed containers in cool, dry area | Prevents moisture pickup and reactivity |
Although CPTi powder is relatively inert compared to reactive metal powders, following precautions is necessary to mitigate safety and fire risks.
CPTi Powder Inspection and Testing
Quality testing ensures CPTi powder meets the required material specifications:
CPTi Powder Testing
| Test | Details |
|---|---|
| Chemistry analysis | ICP spectroscopy verifies elemental composition |
| Particle size distribution | Sieve analysis determines size distribution |
| Apparent density | Measured as per ASTM B212 standard |
| Powder morphology | Scanning electron microscopy verifies spherical shape |
| Flow rate | Time taken for fixed powder quantity to flow through defined nozzle |
| Tap density | Density measured after mechanically tapping powder sample |
| Compressibility | Monitoring of powder bed density change during compression |
Rigorous testing protocols ensure reliable and consistent high performance of CPTi powder for critical applications.
CPTi Powder Storage and Reactivity
CPTi powder has moderate reactivity:
CPTi Powder Storage
| Factor | Effect |
|---|---|
| Air, oxygen | Moderate oxidation risk above 500°C |
| Moisture | Low corrosion rate at room temperature |
| Hydrocarbons | Risk of fire if allowed to contaminate powder |
| Acids, bases | Low corrosion rates in neutral solutions |
| Organic solvents | Some absorption and discoloration if immersed |
| Elevated temperatures | Increased reactivity with oxygen and nitrogen |
Recommendations:
- Store in sealed inert gas filled containers
- Keep below 30°C temperature
- Open containers only in dry, controlled environments
- Limit contact with oxidizing acids and chlorinated hydrocarbons
With proper precautions during storage and handling, CPTi powder exhibits excellent stability and low reactivity.
Comparison With Ti-6Al-4V Alloy Powder
Ti-6Al-4V is a popular alpha-beta titanium alloy powder. Comparison with CPTi:
CPTi vs Ti-6Al-4V Powder
| Parameter | CPTi Powder | Ti-6Al-4V Powder |
|---|---|---|
| Density | 4.5 g/cc | 4.42 g/cc |
| Tensile strength | 420 – 550 MPa | 950 – 1050 MPa |
| Ductility | 15 – 30% | 10 – 18% |
| Fatigue strength | 200 – 300 MPa | 500 – 600 MPa |
| Corrosion resistance | Excellent | Moderate |
| Oxidation resistance | Excellent | Good |
| Cost | Low | Moderate |
| Toxicity | None | Low |
| Uses | Low temperature applications, prosthetics | Aerospace components, automotive parts |
- CPTi provides better ductility and oxidation resistance
- Ti-6Al-4V is stronger with higher fatigue strength
- CPTi has better bio-compatibility and corrosion resistance
- Ti-6Al-4V provides higher strength-to-weight ratio
- CPTi is more cost effective while Ti-6Al-4V offers higher performance
CPTi Powder Pros and Cons
Advantages of CPTi Powder:
- Excellent corrosion resistance
- High strength-to-weight ratio
- Good ductility and fracture toughness
- Non-toxic and biocompatible
- Non-magnetic and thermally stable
- Cost-effective compared to titanium alloys
- Can be alloyed to enhance properties
- Suitable for diverse applications across industries
Limitations of CPTi Powder:
- Relatively expensive compared to iron/steel powders
- Lower strength than titanium alloys
- Moderate high temperature oxidation resistance
- Requires protective atmospheres during processing
- Susceptible to galling and seizure in sliding contact
- Harder to machine compared to steels and aluminum alloys
CPTi Powder FAQs
Q: What are the main advantages of CPTi powder?
A: The main advantages are high strength, low density, excellent corrosion resistance, biocompatibility, thermal stability and cost-effectiveness.
Q: What are the typical applications of CPTi powder?
A: Major applications are orthopedic implants, dental implants, aerospace components, automotive parts, sporting goods, jewelry, chemical equipment, and medical devices.
Q: What are the differences between various CPTi powder grades?
A: Higher purity powder grades (grade 3 and 4) are used for medical implants and high performance applications. Lower grades provide adequate properties at lower cost for industrial uses.
About Met3DP
Product Category
HOT SALE
CONTACT US
Any questions? Send us message now! We’ll serve your request with a whole team after receiving your message.