概述 MIM 制造
金属注射成型(MIM)是一种粉末冶金制造工艺,用于大批量生产小型、复杂的金属零件。
MIM 的关键步骤包括
- 将细金属粉末与粘合剂混合制成原料
- 使用注塑成型技术将原料注入模具中
- 除胶,去除粘合剂,只留下金属粉末
- 烧结将粉末致密化为固体金属部件
MIM 结合了注塑成型的设计灵活性和机加工金属的强度和性能。对于复杂的小零件大批量生产来说,这是一种经济高效的工艺。
MIM 制造的工作原理
MIM 制造工艺包括
- 通过将精细金属粉末与聚合物粘合剂混合并造粒来配制原料
- 加热原料并注塑成所需形状
- 通过溶剂或热脱胶化学去除粘合剂
- 在熔炉中烧结去毛刺的金属部件,生产出完全致密的部件
- 可选的二次精加工工序,如机加工、钻孔、电镀
金属射出成型可以经济地生产具有复杂几何形状、严格公差和优异机械性能的部件。
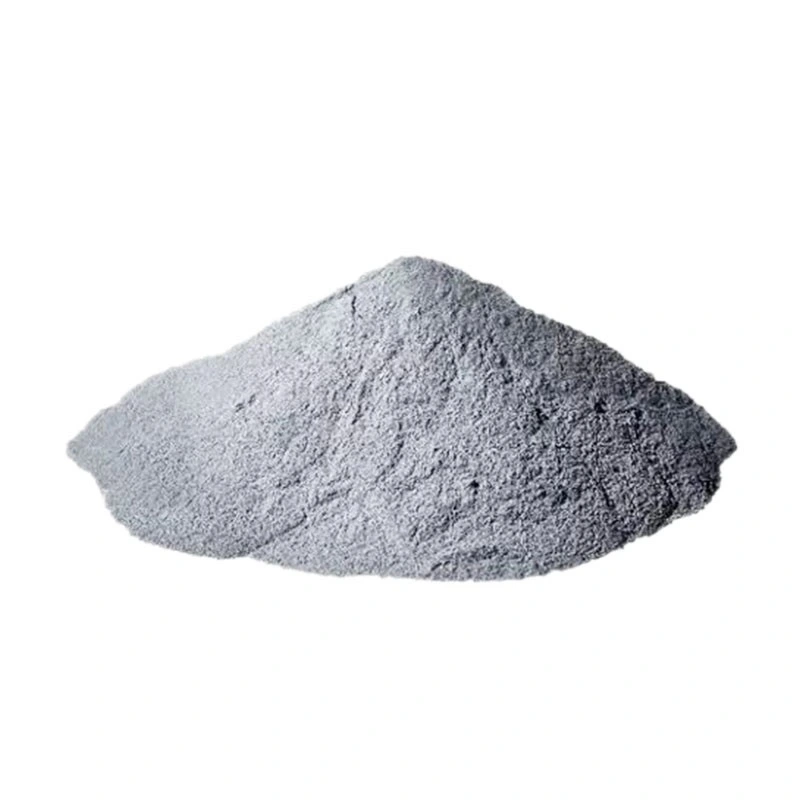

金属射出成型中使用的金属类型
MIM 技术可加工多种金属:
- 不锈钢 - 316L、17-4PH、410、420
- 工具钢 - H13、P20、A2、D2
- 磁性合金 - 软硬铁氧体
- 铜合金 - 黄铜、青铜
- 低合金钢 - 4100、4600
- 超耐热合金 - Inconel 625、718
- 钨重合金
- 钛合金 - Ti6Al4V、Ti6Al4V ELI
MIM 通常适用于任何可烧结成高密度的材料。熔点低于 1000°C 的金属是首选。
MIM 制造工艺参数
金属射出成型的关键工艺参数包括
原料开发:
- 粉末形态、粒度分布
- 粘合剂成分
- 粉末装载量 - 通常为 60-65 vol%
- 混合过程 - 温度、时间、气氛
成型:
- 模具材料 - P20 工具钢优先
- 喷射温度、压力和速度
- 闸门设计
- 冷却系统设计
除胶:
- 溶剂、热或催化脱胶
- 脱胶温度、时间、气氛
烧结:
- 温度曲线 - 脱脂、烧结步骤
- 加热速率、烧结时间、气氛
- 烧结温度和压力
MIM 设计和部件注意事项
MIM 工艺允许自由设计,但必须遵守一些准则:
- 壁厚:0.3 - 4 毫米之间均可
- 表面光洁度:砷烧结的表面粗糙度约为 Ra 1.5 μm
- 尺寸公差:标准为 ±0.5%,也可达到 ±0.1%
- 避免残留粉末:没有完全封闭的内腔
- 吃水角度:> 1° 吃水角更佳
- 烧结收缩率约 20% 体积收缩率
- 减少缺陷:较大的转角半径可最大限度地减少裂缝
先进的模拟工具可以在设计过程中对 MIM 流程进行虚拟优化,从而减少试验和错误。
的好处 MIM 制造
利用 MIM 的主要优势包括
- 复杂的几何形状和严格的公差
- 卓越的机械性能
- 多种材料可供选择
- 生产量大,成本低
- 最大限度地减少浪费--近净成形工艺
- 减少机加工和精加工
- 组件集成和部件整合
- 适合熄灯操作的自动化流程
- 比机械加工更环保
- 可从原型扩展到全面生产
这些优势使 MIM 适合于各行各业经济高效地大批量制造精密金属部件。
计量信息模型的局限性和挑战
与 MIM 有关的一些限制:
- 尺寸有限 - 每个部件的成品质量通常小于 45 克
- 仅限于能烧结成高密度的金属
- 需要丰富的原料配方专业知识
- 模具和工艺开发的前期成本
- 直线部分和尖角容易开裂
- 与其他工艺相比,准备时间较长
- 通常需要进行后处理才能获得最终特性
- 某些功能(如线程)的设计缺乏自由度
- 对烧结金属进行二次加工具有挑战性
只要针对应用进行适当的原料和工艺设计,就能克服这些挑战,充分发挥 MIM 技术的潜力。
MIM 制造部件的应用
MIM 在以下领域得到广泛应用:
汽车:锁具硬件、传感器、燃料系统和发动机部件
航空航天:叶轮、喷嘴、阀门、紧固件
医疗:牙科植入物、手术刀手柄、整形外科器械
枪支:扳机、弹夹、滑轨、击锤
手表:表壳、手镯链节、表扣和带扣
电气:确保可靠性的连接器和引线框架
典型的零件尺寸从 0.1 克到 110 克不等,商业产量最大的是连接器、紧固件、手术器械和正畸支架。
金属射出成型制造成本分析
金属射出成型制造成本包括
- 原料开发 - 配制、混合、表征
- 模具制造 - 高精度模具加工
- MIM 机器 - 大型资本设备投资
- 运行 - 人工、水电、消耗品
- 二级运行 - 脱脂、烧结、精加工
- 材料利用率 - 金属粉末约占总成本的 60%
- 消耗性工具 - 多个模腔可实现大批量生产
- 生产量 - 设置成本按总量摊销
- 买飞比 - 与其他 PM 流程相比,仅为 2-4 倍
- 设计优化 - 几何形状简单,机加工量极少
对于大批量生产,金属射出成型技术能以极高的生产率、出色的材料利用率和接近净成形的能力,提供非常有利的成本。
选择 MIM 制造 合作伙伴
选择 MIM 供应商的关键因素:
- 已证明的专业知识和多年的 MIM 经验
- 材料组合 - 一系列不锈钢、工具钢和超级合金选项
- 质量认证 - 最好是 ISO 9001、ISO 13485
- 二次加工能力 - 机加工、热处理、表面精加工
- 严格的工艺和产品质量控制程序
- 原料配方和工艺开发的研发能力
- 模流模拟和其他设计分析专业知识
- 支持客户项目的计划管理技能
- 可扩展的生产能力,能够随着生产需求的增长而增长
- 具有竞争力的多年期协议定价
- 可进行密切合作和知识产权保护的地点
与一般的 CNC 金属加工店相比,选择一家专注于 MIM 的成熟 MIM 生产商将能获得最佳效果。
MIM 与 CNC 加工的优缺点
MIM 的优势:
- 卓越的尺寸精度和可重复性
- 机加工无法实现的复杂几何形状
- 近似网状,材料浪费最少
- 可高效扩展至极高产量
- 自动化流程实现全天候运行
- 设置完成后的交付周期更短
- 大幅降低大批量生产时的零件成本
- 性能达到或超过机加工金属
多模态集成电路的缺点:
- 原料和模具的初始设置成本较高
- 尺寸有限的功能
- 某些功能的设计自由度受到限制
- 初始生产量较低,效率不高
- 需要丰富的原料配方专业知识
- 可能仍需进行二次加工
- 初始原型的交付周期较长,质量较低
对于大批量生产的小型复杂金属零件,金属射出成型是最省时省力的制造方法。
MIM 与金属三维打印的比较
MIM 与 3D 打印的主要区别
| 参数 | MIM | 三维打印 |
|---|---|---|
| 过程 | 粘合剂注塑 + 烧结 | 粉末床融合或粘结 |
| 材料 | 多种合金 | 材料选择有限 |
| 部件尺寸 | < 45 克 | 多达几公斤 |
| 准确性 | 优秀,±0.5% | 中度,±1% |
| 表面处理 | 非常好 | 中差 |
| 生产规模 | 万至百万 | 从原型制作到中等批量生产 |
| 每个部件的成本 | 非常低 | 中至高 |
| 二次精加工 | 可能需要 | 通常需要 |
| 准备时间 | 工艺开发时间更长 | 原型制作速度更快,但批量生产速度较慢 |
常见问题
MIM 制造的典型公差能力是多少?
MIM 可以可靠地实现 ±0.5% 的尺寸公差,先进的工艺可以实现小型精密部件 ±0.1% 的公差。
常见的 MIM 原料成分有哪些?
典型的 MIM 原料包括 60-65% 的金属粉末和 35-40% 的粘合剂,粘合剂包括聚丙烯、聚乙烯和聚苯乙烯等聚合物。蜡有助于改善粉末流动性。
MIM 能用多种材料制造零件吗?
是的,通过在每个模腔中注塑不同的原料或使用不同熔点的粘合剂,金属射出成型可以生产出复合结构和分级结构。
利用 MIM 可以实现多大的成型零件尺寸?
MIM 模塑通常仅限于质量小于 45 克、尺寸小于 50 毫米的部件。较大或较重的部件很难充分填充和致密化。
就小型金属部件而言,MIM 与压铸相比如何?
金属射出成型的尺寸精度和材料强度更高,但压铸的周期更快。金属射出成型更适合复杂的几何形状,而压铸更适合简单的形状。


