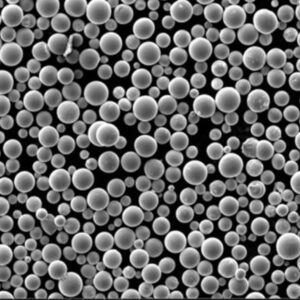
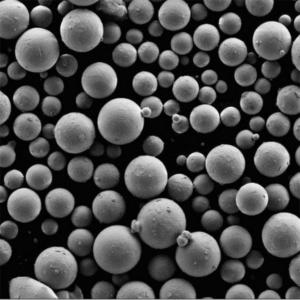
概述
增材制造(AM)又称三维打印,利用金属粉末根据数字模型逐层制造部件。粉末作为原料,在 CAD 几何图形的引导下,通过精密热源有选择性地熔化、烧结或结合。
常用的金属 AM 工艺包括粘合剂喷射、定向能沉积、粉末床熔融和薄片层压。每种技术都需要具有特定特性的粉末,以实现打印部件的最佳密度、表面光洁度、尺寸精度和机械性能。
本指南深入介绍了用于 AM 的金属粉末,包括合金选择、生产方法、关键粉末特性、应用、规格、供应商以及采购材料时的注意事项。有用的对照表总结了有助于粉末选择和鉴定的技术数据。
采购优化的 AM 粉末可使制造商提高打印质量、减少缺陷,并充分发挥 3D 打印的优势,如设计自由度、更快的迭代和零件整合。与知识渊博的供应商建立联系可简化原材料鉴定。

AM 粉末的合金选择
有多种金属和合金可作为 3D 打印工艺的优化粉末原料:
通用合金系统 快速成型制造粉末
- 不锈钢
- 工具钢
- 钛和钛合金
- 铝合金
- 镍超合金
- 钴铬合金
- 金、银等贵金属
- 铜、钽、钨等异种合金
我们可以采购标准合金和定制合金,以满足在耐腐蚀性、强度、硬度、导电性或其他性能方面的特定需求。
用于 AM 的金属粉末生产方法
快速成型技术利用金属粉末进行生产:
用于 AM 的典型金属粉末制造方法
- 气体雾化
- 水雾化
- 等离子雾化
- 电解
- 羰基铁工艺
- 机械合金化
- 金属氢化/脱水
- 血浆球体化
- 造粒
球形雾化粉末可提供大多数 AM 工艺所需的最佳流动性和致密堆积。某些技术可实现纳米级或定制合金颗粒。
AM 金属粉末的主要特点
调制解调器的关键粉末特性包括
金属 快速成型制造粉末 属性
| 特征 | 典型值 | 重要性 |
|---|---|---|
| 粒径分布 | 10 至 45 微米 | 影响致密化和表面光洁度 |
| 粒子形状 | 球形 | 改善粉末流动和包装 |
| 表观密度 | 2 至 4 克/立方厘米 | 影响粉末床密度 |
| 水龙头密度 | 3 至 6 克/立方厘米 | 表示可压缩性 |
| 霍尔流量 | 25-50 秒/50 克 | 确保顺利撒粉 |
| 点火损失 | 0.1-0.5% | 低水分含量可改善印刷效果 |
| 氧气含量 | <0.1% | 最大限度地减少氧化物造成的缺陷 |
精确控制颗粒大小、形状和化学成分等特性对于实现具有所需性能的全致密 AM 部件至关重要。
AM 金属粉末的应用
快速成型制造技术可实现传统技术无法实现的复杂几何形状:
金属快速成型制造应用
| 行业 | 用途 | 益处 |
|---|---|---|
| 航空航天 | 涡轮叶片、结构 | 设计自由,重量减轻 |
| 医疗 | 植入物、假肢、器械 | 定制形状 |
| 汽车 | 原型和工具的轻量化 | 快速迭代 |
| 国防 | 无人机部件、防护结构 | 快速原型和短期运行 |
| 能源 | 热交换器、歧管 | 部件合并和拓扑优化 |
| 电子产品 | 屏蔽、冷却装置、EMI | 复杂的封闭结构 |
与传统制造方法相比,轻量化、部件整合和适用于极端环境的高性能合金具有关键优势。
AM 金属粉末的规格
国际规范有助于实现调幅粉末特性的标准化:
增材制造金属粉末标准
| 标准 | 范围 | 参数 | 测试方法 |
|---|---|---|---|
| ASTM F3049 | AM 金属表征指南 | 取样、尺寸分析、化学、缺陷 | 显微镜、衍射、SEM-EDS |
| ASTM F3001-14 | 用于 AM 的钛合金 | 颗粒大小、化学性质、流量 | 筛分、扫描电镜-电子显微镜 |
| ASTM F3301 | 用于 AM 的镍合金 | 颗粒形状和大小分析 | 显微镜、图像分析 |
| ASTM F3056 | 用于 AM 的不锈钢 | 化学、粉末特性 | ICP-OES, pycnometry |
| ISO/ASTM 52921 | AM 粉末的标准术语 | 定义和粉末特性 | 各种 |
遵守已公布的规格,确保为关键应用提供可重复的高质量粉末原料。
AM 金属粉末全球供应商
AM 优化金属粉末的主要国际供应商包括
用于增材制造的金属粉末制造商
| 供应商 | 材料 | 典型粒径 |
|---|---|---|
| 山特维克 | 不锈钢、工具钢、镍合金 | 15-45 微米 |
| 普莱克斯 | 钛、超级合金 | 10-45 微米 |
| AP&C | 钛、镍、钴合金 | 5-25 微米 |
| 木匠添加剂 | 钴铬合金、不锈钢、铜 | 15-45 微米 |
| LPW 技术 | 铝合金、钛 | 10-100 微米 |
| EOS | 工具钢、钴铬合金、不锈钢 | 20-50 微米 |
许多产品都专注于专为普通 AM 方法(如粘合剂喷射、粉末床熔融和定向能沉积)设计的细球形粉末。
AM 金属粉末的采购注意事项
与供应商讨论的主要方面:
- 所需的合金成分和性能
- 目标粒度分布和形状
- 围护结构密度和大厅流动性
- 氧气和水分等杂质的允许含量
- 所需的测试数据和粉末特征
- 可用数量范围和交付周期
- 发火合金的特殊处理注意事项
- 质量体系和粉末来源可追溯性
- AM 粉末要求方面的专业技术知识
- 物流和交付机制
与在 AM 专用粉末方面经验丰富的供应商密切合作,确保为您的工艺和组件选择理想的材料。
AM 金属粉末的优缺点
用于增材制造的金属粉末的优点与局限性
| 优势 | 缺点 |
|---|---|
| 允许复杂的定制几何形状 | 成本高于传统材料 |
| 大大缩短开发时间 | 所需的粉末处理预防措施 |
| 简化装配和轻量化 | 照样打印的部件通常需要后处理 |
| 达到接近锻造材料的性能 | 尺寸和建造量限制 |
| 无需昂贵的工具 | 热应力可导致开裂和变形 |
| 实现部件整合和拓扑优化 | 生产量低于传统方法 |
| 大大提高购买飞行比率 | 需要严格的粉末表征和参数开发 |
如果使用得当,金属 AM 可以带来改变游戏规则的优势,但需要专业技术才能成功实施。

常见问题
金属增材制造的粒度可以有多小?
专门的雾化技术可以生产出最小 1-10 微米的粉末,但大多数金属打印机的最小尺寸在 15-20 微米左右时效果最佳,这样可以获得良好的流动性和包装效果。
印刷金属零件表面粗糙的原因是什么?
表面粗糙是由于部分熔化的粉末附着在表面上、飞溅、阶梯步进以及熔池特性不理想造成的。使用更细的粉末并调整理想的加工参数可使表面更光滑。
所有金属 3D 打印方法都使用相同的粉末吗?
虽然存在重叠,但与粉末床熔化相比,粘合剂喷射通常使用更广泛的粉末粒度分布。有些工艺根据熔点或反应性仅限于某些合金。
如何制造混合粉末或双金属粉末?
预合金粉末可确保性能均匀,但对于复合材料,物理粉末混合或专门的雾化技术可提供定制的混合元素粉末混合物。
金属打印机更换粉末材料需要多长时间?
不同合金之间的全面清洗和转换通常需要 6-12 个小时。类似材料之间的快速转换则可在一小时内完成。
结论
经过优化的金属粉末使增材制造工艺能够制造出具有优异性能的复杂、坚固的金属部件。将合金化学成分和粉末特性与打印方法和部件性能要求相匹配是获得高质量结果的关键。通过与经验丰富的粉末供应商合作,最终用户可以利用粉末生产和三维打印工艺方面的专业知识,更快、更可靠地开发零件。金属粉末的不断进步有助于推动添加式技术在关键行业的应用。