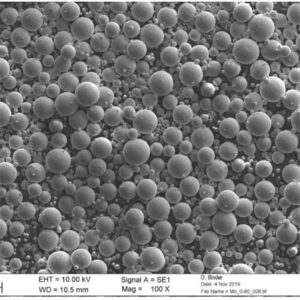
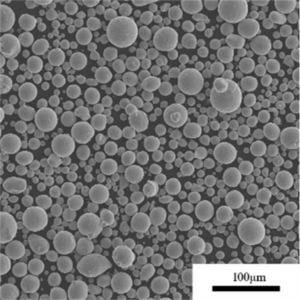
Überblick über gasverdüstes Metallpulver
Gasverdüstes Metallpulver bezieht sich auf metallische Partikel, die durch Zerstäuben von geschmolzenem Legierungsmaterial mit Hochgeschwindigkeits-Inertgasstrahlen hergestellt werden. Dadurch entsteht eine kugelförmige Morphologie, die sich ideal für die additive Fertigung, das Metallspritzgießen und andere Anwendungen eignet.
Merkmale der Gaszerstäubung:
- Ausgezeichnete Kontrolle über Partikelform und Größenverteilung
- Anwendbar auf reaktive Legierungen wie Titan, Aluminium
- Hochreines Ausgangsmaterial für fortschrittliche Prozesse
- Pulver für das heißisostatische Pressen, Wärmebehandlung
- Unterstützt präzise, wiederholbare Pulvereigenschaften
Lesen Sie weiter, um mehr über Zusammensetzungsoptionen, Partikelqualitäten, Verwendungszwecke und Spezifikationen von gaszerstäubten Pulvern zu erfahren.

Legierung Arten von gasverdüstem Metallpulver
Verschiedene Legierungen lassen sich mit Gas zu feinen, kugelförmigen Pulvern zerstäuben:
| Kategorie Legierung | Materialien | Kompositionen |
|---|---|---|
| Rostfreie Stähle | 304, 316, 17-4PH, 303, 410 | Fe/Cr/Ni + Spurenelemente |
| Werkzeugstähle | H13, M2, M4 | Fe + V, Mo, W Karbide |
| Kobalt-Legierungen | CoCr, CoCrW, CoCrMo | Co/Cr + Wolfram/Molybdän |
| Nickel-Legierungen | Inconel 625 & 718 | Ni/Cr/Fe/Mo |
| Titan-Legierungen | Ti-6Al-4V, Ti-6242 | Ti/Al/V/Sn/Zr/Mo |
Tabelle 1: Überblick über die im Handel erhältlichen Legierungssysteme in gasverdüstem Pulver
Für spezielle additive Fertigungsverfahren und branchenspezifische Legierungen für die Luft- und Raumfahrt sowie die Biomedizin gelten unter Umständen Mindestbestellmengen oder Vorlaufzeiten.
Pulvereigenschaften
Typische Partikeleigenschaften, die durch Inertgaszerstäubung erreicht werden:
| Charakteristisch | Einzelheiten | Bedeutung |
|---|---|---|
| Partikelform | Hochgradig kugelförmig | Verbessert Pulverfluss und Packungsdichte |
| Größenbereich | 10 μm bis 150 μm | Kontrollierte Verteilung, optimiert für den Endverbrauch |
| Zusammensetzung | Legierung innerhalb von ± 0,5 Gew.-% gehalten% | Bewahrt die mechanischen Eigenschaften |
| Reinheit | Bis zu 99,9% erzielbar | Reduziert Verunreinigungen und Einschlüsse |
| Oberflächenoxide | <50 nm dicke Passivierungsschicht | Bewahrt die ausgezeichnete Recyclingfähigkeit des Pulvers |
Tabelle 2: Überblick über die Partikelqualität von gasverdüsten Metallpulvern
Präzise und wiederholbar hergestellte Eigenschaften zur Erfüllung von Zertifizierungsanforderungen in den Bereichen Luft- und Raumfahrt, Medizin, Automobil und Industrie.
Herstellungsprozess
- Typische Schritte bei der Zerstäubung mit Inertgas:
- Induktions- oder Lichtbogenschmelzen bildet Legierungsschmelze unter Schutzgas
- Hochreines Inertgas (Ar oder N2) wird durch spezielle Düsen gepresst
- Der Schmelzestrom zerfällt in feine Tröpfchen, die schnell zu Pulver abkühlen
- Das Pulver setzt sich in den darunter liegenden Sammelbehältern ab.
- Klassifizierung über Siebe zur Normalisierung der Verteilung
- Unter Schutzatmosphäre verpackt und an Kunden versandt
- Kritische Prozessparameter:
- Düsendesign - bestimmt die Partikelgrößenverteilung
- Gasdruck - beeinflusst die Partikelgeschwindigkeit und die Abkühlungsrate
- Gießgeschwindigkeit der Schmelze - beeinflusst die Form der Größenverteilung
- Umgebung (Vakuum vs. kontrollierte Atmosphäre) hängt von der Reaktivität ab
Anwendungen von gasverdüstes Metallpulver
| Anmeldung | Vorteile | Beispiele |
|---|---|---|
| Additive Fertigung | Teile mit hoher Dichte durch exzellenten Pulverfluss und Verpackung | Komponenten für die Luft- und Raumfahrt, medizinische Implantate |
| Metall-Spritzgießen | Gute Formbarkeit für kleine, komplizierte Formen | Turbinenschaufeln, Düsenkomponenten |
| Thermische Spritzschichten | Dichte Beschichtungen aus verformbaren Partikelaufschlägen | Abriebfeste Oberflächen |
| Lötpasten | Komplexe Geometrien verbinden | Wärmetauscher, elektrische Kontakte |
| Heiß-Isostatisches Pressen | Minimierung von Verschlussproblemen bei kugelförmigen Partikeln | Gegossene Turbinenschaufeln konsolidieren |
| Vorläufer für die Wärmebehandlung | Anpassungsfähige Kornstruktur | Ausscheidungshärtende Legierungen |
Tabelle 3: Überblick über Anwendungen, die die Eigenschaften von gaszerstäubten Metallpulvern nutzen
Die Konsistenz und Reinheit, die die Gaszerstäubung bietet, eignet sich für die meisten fortschrittlichen Metallpulverprozesse, bei denen die Wiederholbarkeit entscheidend ist.
Spezifikationen von gasverdüstes Metallpulver
Gasverdüste Pulver werden anhand verschiedener Standardspezifikationen validiert:
| Standard | Beschreibung |
|---|---|
| ASTM B214 | Validierung mittels optischer Mikroskopie auf Gleichmäßigkeit und Satellitenfreiheit |
| AMS 7008 | Spezifikation von Werkstoffen für die Luft- und Raumfahrt, einschließlich Inertgas-Zerstäubungsmethode |
| ASTM F3049 | Standardleitfaden für die Charakterisierung der Eigenschaften von Metallpulvern für AM |
| ASTM F3056 | Spezifikation für Pulver aus Nickellegierungen für die additive Fertigung |
| ISO 21818 | Spezifikation für DMLS/SLM-Produktionsstähle aus nichtrostenden Stählen |
Tabelle 4: Industrienormen, die üblicherweise für mit Inertgas zerstäubte Pulver gelten
Seriöse Hersteller stellen vollständige Zertifizierungsunterlagen und Testergebnisse für jede Pulvercharge zur Verfügung, um die Einhaltung der Vorschriften zu bestätigen.
Lieferanten und Preisgestaltung
| Anbieter | Materialien | Vorläufige Preisgestaltung |
|---|---|---|
| Sandvik Fischadler | Ti-Legierungen, Ni-Legierungen, Werkzeugstähle | $100+ pro kg |
| Zimmerer-Zusatzstoff | Nichtrostende Stähle, Kobaltlegierungen, Cu | $50 - $150 pro kg |
| Praxair | Ti-Legierungen, Al-Legierungen, Silizium-Pulver | $100+ pro kg |
| LPW-Technologie | Werkzeugstähle, rostfreie Stähle, Inconels | $50 - $500 pro kg |
| SLM-Lösungen | Entwicklung kundenspezifischer Legierungen | $250+ pro kg |
Tabelle 5: Auswahl von Unternehmen, die gaszerstäubte Metallpulver liefern, mit ungefähren Preisen
Die meisten Anbieter bieten Standardlegierungen mit Lieferzeiten von 2-4 Wochen in kleinen Mengen an. Kundenspezifische Formulierungen und einzigartige Partikeloptimierung sind ebenfalls möglich, wenn man direkt mit Anbietern von Gaszerstäubungsanlagen zusammenarbeitet.
Vor- und Nachteile gegenüber Alternativen
| Parameter | Gaszerstäubung | Wasserzerstäubung | Plasma-Zerstäubung |
|---|---|---|---|
| Morphologie der Partikel | Hochgradig kugelförmig | Unregelmäßigere Sphäroide | Meist kugelförmig |
| Partikelgrößenverteilung | Enge Verteilung, maßgeschneidert | Weiterer Vertrieb | Enge Verteilung |
| Legierungen kompatibel | Die meisten handelsüblichen Legierungen | Begrenzte Legierungen | Breites Spektrum einschließlich reaktiver Metalle |
| Kosten pro kg | Mäßig $50-150 pro kg | Niedriger $20-100 pro kg | Höher $150-500 pro kg |
| Produktivitätsraten | Kapazität bis zu 10.000 kg pro Tag | Sehr hoch >50.000 kg pro Tag | <1.000 kg pro Tag |
Tabelle 6: Vergleich der Gaszerstäubung mit alternativen Methoden der Pulverherstellung
Die Gasverdüsung bietet ein optimales Gleichgewicht zwischen Leistungsfähigkeit und Wirtschaftlichkeit und liefert Pulvermengen, die für die kommerzielle Produktion geeignet sind.
Beschränkungen
- Minimale Losgrößen erfordern den Einsatz von mehr als 100 kg Material, um die Einrichtung der Maschine zu rechtfertigen.
- Begrenzte Fähigkeit, Legierungen mit hohem Schmelzpunkt wie Wolfram wirtschaftlich zu zerstäuben
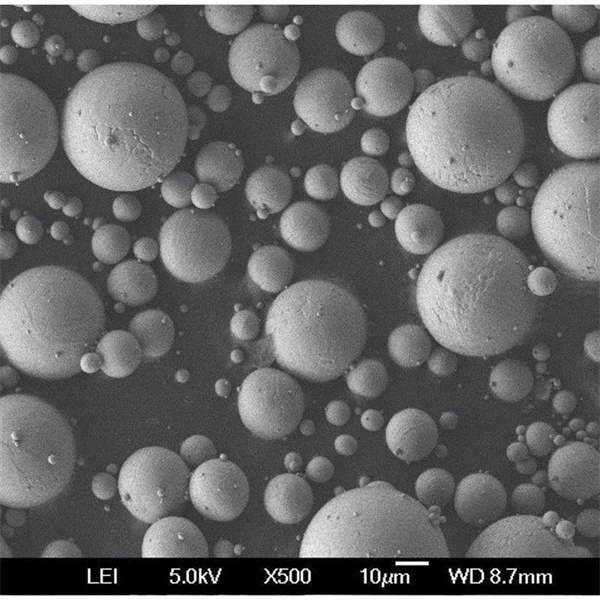
- Die Pulver sind nicht so kugelförmig wie bei der Plasmazerstäubung und enthalten einige Satelliten
- Oxiddicke etwas höher als bei Vakuumplasma-Alternativen
- Steile Anfangskapitalkosten von etwa $1-5 Millionen für ein schlüsselfertiges System
- Erfordert eine verbesserte Handhabung/Lagerung des Pulvers im Vergleich zu ungebrauchten Materialien

FAQ
F: Welchen Vorteil bietet gaszerstäubtes Pulver gegenüber neuen Materialien für die Herstellung von Teilen?
A: Gaszerstäubte Pulver bieten eine hervorragende Konsistenz und Wiederholbarkeit. Die Entwicklung der Pulvermorphologie und der Kornstruktur von Anfang an ermöglicht ausgereifte Prozesse zur Herstellung zertifizierter Komponenten, die den höchsten Anforderungen der Industrie in der Luft- und Raumfahrt und der Medizintechnik entsprechen.
F: Welche Vorsichtsmaßnahmen sind beim Umgang mit gaszerstäubten Pulvern erforderlich?
A: Da es sich um feine metallische Materialien handelt, die zur Oxidation neigen, werden inerte Lagerungs- und Handhabungsprotokolle empfohlen. Dazu gehören feuchtigkeitskontrollierte, mit Argon gefüllte Handschuhkästen und das Tragen von persönlicher Schutzausrüstung, um das Risiko einer Explosion, Inhalation oder Kontamination zu minimieren. Der Kontakt mit Wasser oder organischen Verbindungen ist zu vermeiden. Eine besondere Konstruktion der Anlage ist nicht unbedingt erforderlich, obwohl örtliche Vorschriften gelten können.
F: Welches Maß an Wiederholbarkeit kann bei gaszerstäubten Pulvern von Charge zu Charge erwartet werden?
A: Seriöse Hersteller garantieren eine Pulververteilung innerhalb von ±10% zwischen den einzelnen Chargen. Geringfügige Abweichungen rechtfertigen immer noch eine erneute Optimierung als Standardverfahren, selbst bei demselben Pulverlieferanten, wenn die zulässigen Komponententoleranzen eng sind. Analysezertifikate dokumentieren die Konsistenz.
F: Wie lange können unbenutzte gaszerstäubte Pulver aufbewahrt werden?
A: Am besten wird das Pulver unter Argon in versiegelten Behältern gelagert, um extreme Temperaturen zu vermeiden. Bei einer Temperatur von unter 30 °C und einer relativen Luftfeuchtigkeit von 50% mit minimalem Sauerstoff- und Feuchtigkeitsgehalt hält sich das Pulver viele Monate, bevor es in der Handschuhbox aufgefrischt werden muss, um die Fließ- und Wiederverwendungseigenschaften zu erhalten.
F: Welche technische Unterstützung bieten Pulverhersteller für die Qualifizierung und Zertifizierung von Teilen?
A: Seriöse Anbieter verfügen über Materialwissenschaftler und Validierungsmitarbeiter, die Anwendungshinweise geben und die Schnittstelle zu den Käufern von Teilen während des Prüfverfahrens zur Zertifizierung von Pulvern bilden. Sie wollen eine nachgewiesene Wiederholbarkeit, die den regulierten Normen entspricht, um die Verwendung von Materialien in anspruchsvolleren Anwendungen zu erweitern. Erwarten Sie von jedem etablierten Anbieter detaillierte Unterlagen und Protokolle.